What Is a Subnet Mask and Why It Still Matters
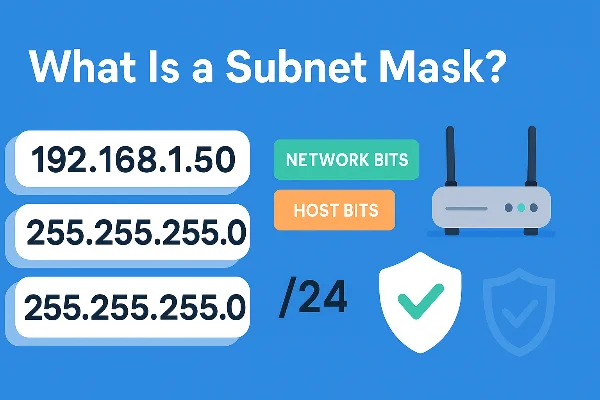
The fastest way to answer what is a subnet mask is this: it’s a binary filter paired with your IP address that marks which bits identify the network and which bits identify the host.
-
In IPv4, the mask is written in dotted-decimal, e.g.,
255.255.255.0. -
In IPv6, you’ll typically see a prefix length like
/64that serves the same purpose.
Why it still matters: a clear mask keeps local traffic local, reduces broadcast noise, and lets admins carve one physical network into multiple subnets for security and performance. Even if you mainly care about privacy tools, grasping what is a subnet mask will make your router and Wi-Fi settings far less mysterious.
How Subnet Masks Work: Network Bits vs Host Bits

Think of an IPv4 address as four octets, e.g., 192.168.1.50. Pair it with the mask 255.255.255.0 and you’ve got:
-
255.255.255→ twenty-four 1-bits (11111111.11111111.11111111) marking the network. -
.0→ eight 0-bits (00000000) marking the host range inside that network.
Your device ANDs the destination IP with the mask. If the result matches its own network ID (e.g., 192.168.1.0), it’s local; otherwise the packet goes to the default gateway. That’s the whole magic behind what is a subnet mask: a quick test that decides “talk directly” vs “ask the router.”
Why this logic matters
-
Keeps local devices (printers, NAS, TVs) talking efficiently.
-
Enables clean segmentation—guest Wi-Fi, IoT, and departments can live on separate subnets.
-
Prevents accidental cross-talk and reduces broadcast storms on busy LANs.
CIDR Notation vs Legacy Classes: The Modern Way to Subnet
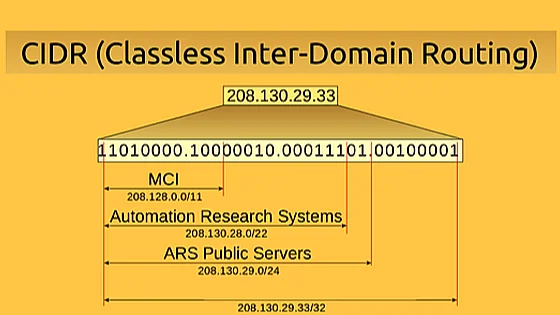
When people ask what is a subnet mask, the next question is usually CIDR notation. Instead of old “classes” (A/B/C), modern networks use Classless Inter-Domain Routing to specify the number of network bits directly:
-
/24=255.255.255.0 -
/23=255.255.254.0 -
/16=255.255.0.0
CIDR makes addressing flexible and avoids wasting IP space. In IPv6, you’ll commonly see /64 for end networks—same concept, far more room. Understanding CIDR turns what is a subnet mask from trivia into a tool you’ll apply daily.
Common Subnet Masks and Quick Math You’ll Actually Use
Below are popular IPv4 masks. Usable hosts exclude the network ID and broadcast address.
| CIDR | Mask | Usable Hosts | Typical Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| /30 | 255.255.255.252 | 2 | Router point-to-point links |
| /29 | 255.255.255.248 | 6 | Small device clusters |
| /28 | 255.255.255.240 | 14 | Small offices, VLANs |
| /27 | 255.255.255.224 | 30 | Departmental subnet |
| /26 | 255.255.255.192 | 62 | Larger segments |
| /24 | 255.255.255.0 | 254 | Home/SMB default |
| /16 | 255.255.0.0 | 65,534 | Big private networks |
Mental math tip: Each time you “borrow” one host bit for the network (e.g., /24 → /25), you halve host capacity and double the number of subnets. That one trick makes what is a subnet mask much easier to reason about.
How to Find or Change Your Subnet Mask on Any Device
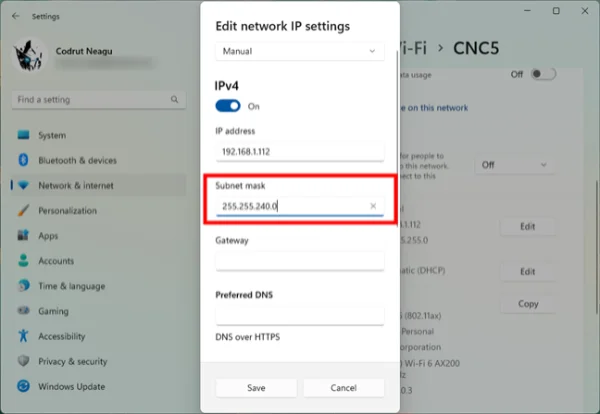
After learning what is a subnet mask, you’ll want to confirm it on your gear.
Windows
-
Open Command Prompt →
ipconfig→ see Subnet Mask under your active adapter.
macOS
-
System Settings → Network → your interface → Details → TCP/IP; or run
ifconfigin Terminal.
Linux
-
Use
ip addr(shows CIDR, e.g.,192.168.1.50/24). Convert/24to255.255.255.0if a dotted mask is needed.
iOS / Android
-
Open Wi-Fi details for the connected network; you’ll see IP, mask/prefix, gateway.
Routers
-
Log into your router (often
192.168.0.1or192.168.1.1) and check LAN or DHCP settings to view or edit the subnet mask and pool range.
When to change it
-
You’re separating guest Wi-Fi or IoT into their own subnets.
-
You’re outgrowing a
/24and need a bigger or smaller pool. -
You’re aligning new VLANs with right-sized networks for performance or policy.
Subnet Mask vs VPN: Different Jobs, Better Together

A common misconception is that a mask hides you online. It doesn’t—so part of answering what is a subnet mask is clarifying what it isn’t.
-
A subnet mask is about routing scope: it defines which IPs live on your local network and which require a router.
-
A VPN encrypts your traffic end-to-end between your device and a VPN server, hides DNS lookups from local observers, and can present a different public IP/region.
Use both for a solid foundation: the mask shapes your LAN; a VPN protects your traffic off-LAN. If you want a fast, beginner-friendly option, A free proxy VPN in UFO VPN offers simple apps, modern protocols, and up to 6 devices per account—great for keeping public-Wi-Fi sessions private while you tinker with home networking.
🌟UFO VPN quick start🌟
UFO VPN is an all-in-one VPN that offers unlimited access to 4D streaming like Netlfix, Disney Plus, no-ping gaming as PUBG, Roblox, CODM and social networking for YouTube, X, Facebook and more.
Unlock Pro Features
If you have upgraded to premium plan , feel free to enjoy premium servers for 4K streaming and advanced features like Kill Switch, Split Tunneling, and gaming acceleration. Your Mac is now fully optimized and protected. Inaddition to basic functions, we recommend you turn on

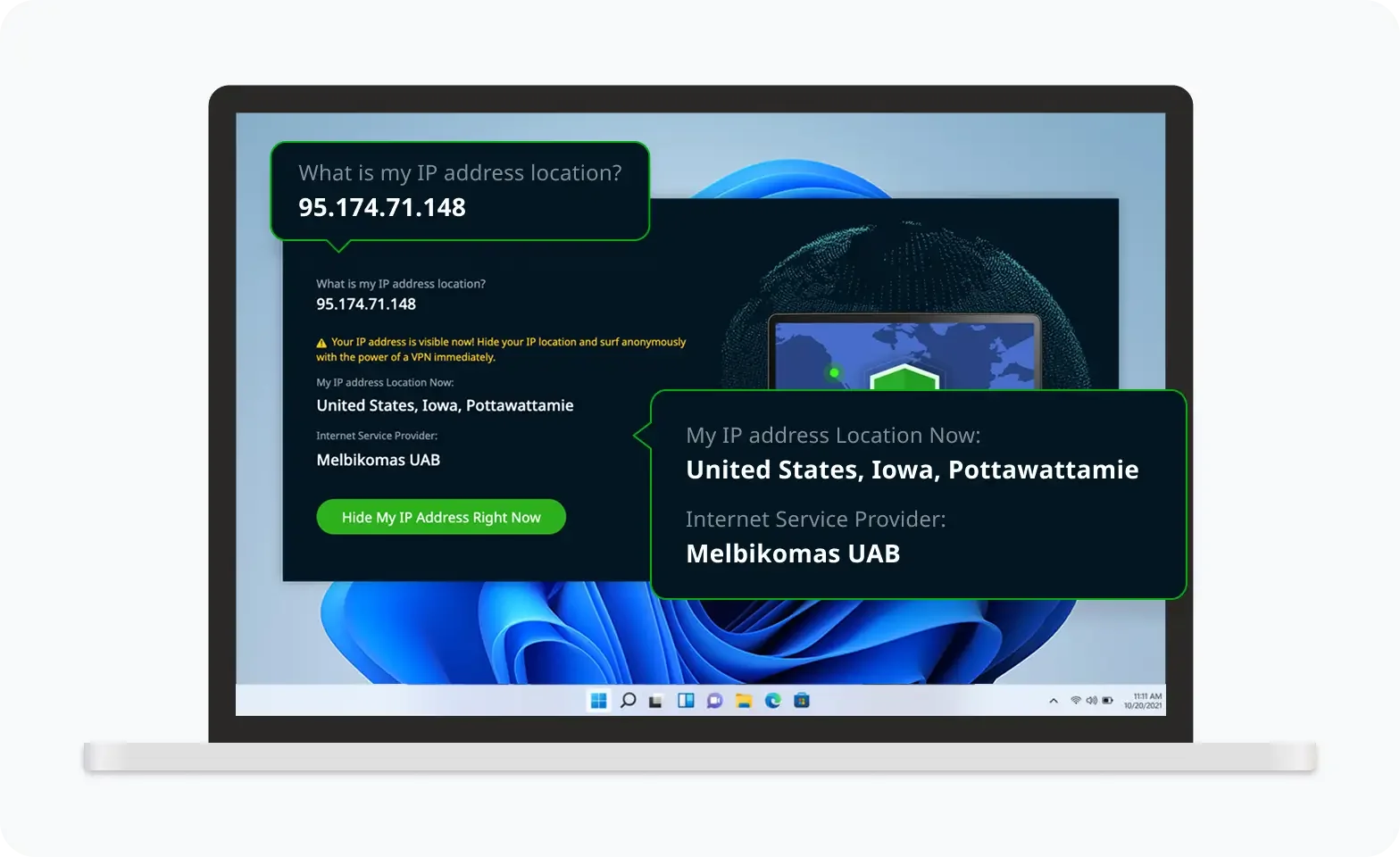
Verify Your IP Now
Use UFO VPN's " What is My IP " feature to see your new IP and location. This confirms your connection is secure, anonymous, and ready for safe browsing online anywhere at any time.

Fixing Subnet Mask Errors: Fast Checks and Remedies
Even pros mess up masks. These quick tests resolve most issues tied to what is a subnet mask:
-
Can’t reach a neighbor device: Two hosts on the same switch but with different prefixes (e.g.,
/24vs/25) will behave like they’re on different networks. Normalize masks on both devices. -
Gateway mismatch: If your PC’s network ID (mask-applied) doesn’t match the gateway’s network, traffic won’t route. Put the gateway inside the same subnet or adjust the mask.
-
Overlapping subnets across VLANs: Overlaps cause routing ambiguity and ARP chaos. Realign masks so each VLAN has a unique network ID.
-
Too-large broadcast domains: Giant
/16segments can drown in broadcasts. Subnet or VLAN-split to reduce noise. -
IPv6 confusion: End networks typically use
/64. Unusual prefixes can break SLAAC and neighbor discovery—stick with common sizes unless you know why you’re changing them.
FAQs
What is a subnet mask in one sentence?
A pattern of bits that splits an IP into network vs host, telling your device whether to talk locally or forward to a router.
How does CIDR relate to what is a subnet mask?
CIDR expresses the mask as a prefix length (e.g., /24), making it easy to size networks without legacy classes.
What’s the most common home mask and why?
255.255.255.0 (/24)—it offers up to 254 usable hosts, perfect for typical home/SMB LANs.
Does a subnet mask protect privacy like a VPN?
No. A mask organizes routing inside your LAN. A VPN encrypts traffic, hides DNS lookups from local observers, and can change public IP/region.
Is IPv6 different for what is a subnet mask?
IPv6 uses prefixes (e.g., /64) instead of dotted masks, but the concept—network vs interface bits—remains the same.
I changed masks and lost access to my router—now what?
Reconnect to the router’s subnet (static IP or DHCP in the right range), or factory-reset if you’ve locked yourself out. Then reapply the correct mask carefully.