Hashing vs Encryption: The Quick Answer
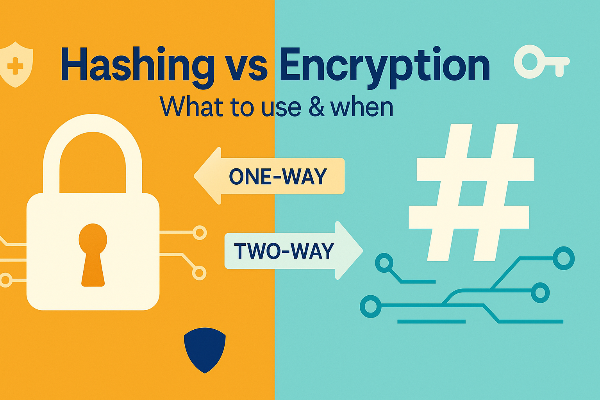
At a glance, hashing vs encryption comes down to direction and intent.
-
Hashing converts data into a fixed-length “digest.” It’s one-way (practically irreversible) and used for verification, like password storage and file integrity.
-
Encryption transforms data so only authorized parties can read it. It’s two-way (reversible with a key) and used for confidentiality, like messages, backups, and network traffic.
Think of hashing vs encryption like stamping a wax seal (hashing) versus locking a box (encryption). A seal shows whether the message was altered; a lock keeps the message private.
What Hashing Really Does

To understand hashing vs encryption, start with hashing’s properties:
-
Deterministic: Same input → same output.
-
Fixed length: Output has a consistent size regardless of input.
-
Avalanche effect: Tiny input changes create very different outputs.
-
One-way: You don’t “decrypt” a hash in the traditional sense.
Everyday uses where hashing wins in “hashing vs encryption”:
-
Password storage: Sites store a salted hash, not the actual password. When you log in, your password is hashed again and the digests are compared.
-
File integrity checks: Download pages share a checksum (e.g., SHA-256). If your hash matches, the file wasn’t altered.
-
Deduplication & indexing: Systems quickly detect identical content by comparing hashes.
Avoid these pitfalls:
-
Don’t use obsolete or fast hashes for passwords (e.g., plain SHA-1/SHA-256 alone). Use slow, memory-hard schemes (argon2id/bcrypt/scrypt).
-
Always include a salt (unique random value) so two identical passwords don’t share the same digest.
When choosing hashing vs encryption, hashing wins whenever you only need to verify, not recover, the original data.
What Encryption Really Does
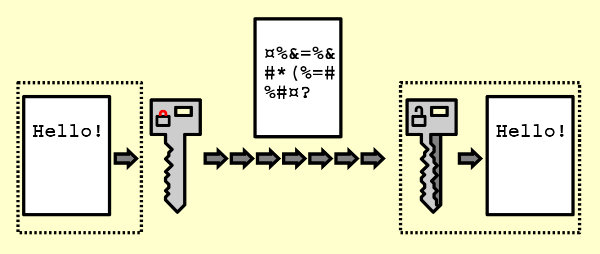
Encryption is the other half of hashing vs encryption—it protects confidentiality by making data unreadable without a key.
-
Symmetric encryption: One secret key encrypts and decrypts. It’s fast and ideal for large volumes (e.g., full-disk encryption, VPN tunnels).
-
Asymmetric encryption (public-key): A public key encrypts, a private key decrypts (or signs). It’s essential for secure key exchange, digital signatures, and certificates.
This is where symmetric vs asymmetric encryption fits inside hashing vs encryption: symmetric handles bulk data; asymmetric solves identity, signatures, and key distribution. Most systems combine them—public-key to agree on secrets, symmetric for the heavy lifting.
When encryption is the right answer in hashing vs encryption:
-
Messaging and email: Data must be readable by the recipient later.
-
Backups and archives: You’ll decrypt them in the future.
-
Network connections: HTTPS, SSH, and VPNs encrypt in transit.
Hashing vs Encryption Difference: Side-by-Side
To anchor hashing vs encryption difference, keep this mental model:
-
Goal: Hashing = integrity/verification; Encryption = confidentiality.
-
Direction: Hashing = one-way; Encryption = reversible with a key.
-
Typical output: Hashing = fixed-length digest; Encryption = ciphertext similar in size to input (plus overhead).
-
Key use: Hashing = none for verification (but do use salt/pepper in password hashing); Encryption = keys are mandatory.
-
Best fit: Hashing for passwords & integrity; Encryption for messages, storage, and transport.
This framing helps you choose confidently whenever hashing vs encryption appears in a design review, spec, or procurement note.
Hashing vs Encryption in Real Scenarios

You’ll encounter hashing vs encryption in everyday tasks. Here’s how to pick:
-
User authentication
-
Use hashing (specialized password hashing). Store salted argon2id/bcrypt/scrypt digests, not plain hashes or encrypted passwords.
-
Why not encryption? Because you should never need the original password—verification is enough.
-
-
API tokens and secrets at rest
-
Use encryption so services can retrieve the secret when needed.
-
Optionally store an additional hash of the secret for quick, constant-time comparisons without exposing the decrypted value anywhere it isn’t required.
-
-
File downloads and software updates
-
Publish hashes (e.g., SHA-256) to verify integrity after download.
-
Distribute updates over encrypted channels (HTTPS) to protect against tampering in transit.
-
-
Backups & exports
-
Encrypt backups; keep keys in a separate secure location.
-
Hash archives to detect corruption over time.
-
-
Messaging, calls, streaming
-
Encrypt in transit (TLS, SRTP, VPN). Hashing adds integrity internally (message authentication codes), but confidentiality is the main goal.
-
Notice how hashing vs encryption are complementary—not competitors.
Hashing vs Encryption in Transit: Where a VPN Fits
You’ll see hashing vs encryption at the network layer every day without noticing it. HTTPS uses public-key cryptography to exchange secrets, then symmetric encryption for speed. A VPN protects all app traffic, not just browser tabs.
How UFO VPN aligns with hashing vs encryption
-
A VPN like free proxy VPN in UFO VPN uses strong encryption to wrap your internet traffic in an encrypted tunnel. That helps on public Wi-Fi, shared networks, or travel where on-path actors might snoop or inject content.
-
It complements hashing used elsewhere (e.g., TLS message authentication, integrity checks). The VPN handles confidentiality in transit, while hashing remains the tool for integrity and password storage.
-
⚠️Practical tip: Following Next 4 Steps to Get Your Encryption Tools⬇️
UFO VPN is an all-in-one VPN that offers unlimited access to 4K streaming like Netlfix, Disney Plus, no-ping gaming as PUBG, Roblox, CODM and social networking for YouTube, X, Facebook and more.
Unlock Pro Features
If you have upgraded to premium plan , feel free to enjoy premium servers for 4K streaming and advanced features like Kill Switch, Split Tunneling, and gaming acceleration. Your Mac is now fully optimized and protected. Inaddition to basic functions, we recommend you turn on

Verify Your IP Now
Use UFO VPN's " What is My IP " feature to see your new IP and location. This confirms your connection is secure, anonymous, and ready for safe browsing online anywhere at any time.

A VPN doesn’t replace good password hashing or key management; it strengthens the in-transit piece of the hashing vs encryption puzzle.
Best Practices You Should Actually Use
Here’s a concise checklist you can apply today—rooted in the hashing vs encryption difference:
-
Passwords: Use argon2id/bcrypt/scrypt with unique salts; consider a global pepper stored in a secure service.
-
Keys: Rotate encryption keys on a schedule; store them separately from data.
-
Algorithms: Prefer modern, vetted choices; avoid home-grown crypto.
-
Integrity: Use HMACs (hash-based message authentication codes) when you need to verify authenticity along with integrity.
-
Backups: Encrypt at rest, hash for verification, and test restore regularly.
-
Transport: Use TLS everywhere; add VPN for full-tunnel coverage on untrusted networks (e.g., UFO VPN when traveling).
-
Audits: Log access to keys/secrets; review configs after major updates.
With these habits, you won’t be forced to choose hashing vs encryption—you’ll deploy each where it’s strongest.
FAQs
What’s the simplest way to remember hashing vs encryption?
Hashing = one-way verification (integrity). Encryption = two-way confidentiality (privacy). That’s the essence of hashing vs encryption difference.
Should I encrypt or hash my users’ passwords?
Hash them using a password-hashing scheme (argon2id/bcrypt/scrypt) with unique salts. Never store or encrypt raw passwords.
Where do symmetric vs asymmetric encryption fit?
They’re building blocks inside encryption. In symmetric vs asymmetric encryption, symmetric handles fast bulk data; asymmetric handles identity, key exchange, and signatures—often both are used together.
Is Base64 encryption?
No. In the hashing vs encryption vs encoding comparison, Base64 is just encoding. It’s for representation, not security.
How do I verify a download safely?
Download over HTTPS (encrypted) and compare the file’s published hash (integrity). That’s hashing vs encryption working together.