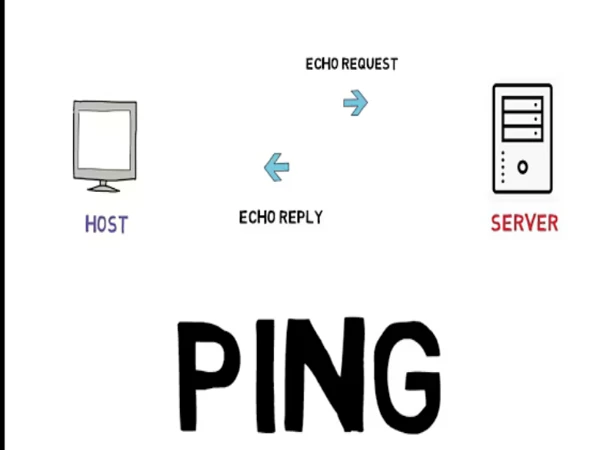
What Is a Ping Command?
Before we dive into practical steps, it’s important to understand what ping actually does. Ping isn’t just a random command; it’s a fundamental part of network diagnostics.
The Technology Behind Ping (ICMP)
Ping uses ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol) to send “echo request” packets to a target (like a website or server) and waits for “echo reply” packets. The time it takes to receive a reply is measured in milliseconds (ms).
For example:
- 20–50 ms → Excellent (ideal for gaming and video calls)
- 50–150 ms → Acceptable for browsing and streaming
- 150 ms+ → Noticeable lag, potential network issues
This mechanism allows users to quickly test if a destination is reachable and how responsive it is.
Key Use Cases for Pinging
So, when should you use ping? Here are the most common scenarios:
✅ Checking connectivity – Verify if your device can reach the internet or another computer.
✅ Diagnosing lag – Gamers use ping to measure latency to servers.
✅ Testing server uptime – IT teams ping servers to ensure availability.
✅ Troubleshooting VPN issues – If your VPN (like UFO VPN) feels slow, ping helps determine if the issue is local or with the VPN server.
How to Ping on Any Device
Since ping is a universal tool, you’ll find it on nearly every platform. The steps vary slightly depending on the operating system, but the principle remains the same.
Windows 10 & 11 (Command Prompt & PowerShell)
- Open Command Prompt (press Win + R, type cmd, and hit Enter).
- Type ping google.com and press Enter.
- You’ll see reply times in milliseconds, which reflect your latency.
Alternatively, PowerShell works the same way.
macOS & Linux (Terminal)
- Open Terminal.
- Enter ping -c 4 google.com to send four packets.
- Review the average latency displayed after the test finishes.
iPhone & Android (Using Apps)
On mobile devices, ping isn’t built-in. Instead, use apps like PingTools or Fing, which provide not only ping but also traceroute and network scanning features. Handy when you’re testing Wi-Fi on the go 📱.
Interpreting Your Ping Results
Running a ping test is easy. The real challenge is understanding what the numbers mean.
Understanding Latency and Packet Loss
- Latency (ms) – The time data takes to travel. Lower is better.
- Packet loss (%) – If packets are missing, it signals unstable connections.
- Fluctuations (jitter) – Large variations in ping times can cause lag spikes.
Here’s a quick reference:
| Result Type | What It Means | Action Needed |
|---|---|---|
| Low latency (20–50 ms) | Excellent | No issues |
| Moderate latency (50–150 ms) | Usable |
Monitor for spikes |
| High latency (150 ms+) | Laggy | Check network or VPN server |
| Packet loss (>2%) | Unstable |
Troubleshoot Wi-Fi or ISP |
Solving Common Ping Errors
Some typical error messages include:
- Request timed out – Destination unreachable, firewall blocking, or poor connection.
- Destination host unreachable – Wrong IP or routing issue.
- General failure – Local adapter or DNS misconfiguration.
If you’re using a VPN like UFO VPN and get unusual errors, try switching servers. A congested VPN node often causes packet loss or high latency.
Advanced Networking Tips
Once you’re comfortable with basic pings, you can step up your diagnostics with advanced commands.
Continuous Ping and Custom Packet Tests
- On Windows: type ping google.com -t for a continuous test.
- On macOS/Linux: just type ping google.com (no count limit).
- To simulate heavy data, use ping google.com -l 1024 on Windows to send larger packets.
This helps evaluate stability for streaming or gaming conditions.
Using Traceroute for Deeper Diagnosis
While ping shows latency, traceroute shows the exact path your data takes.
- Windows: tracert google.com
- macOS/Linux: traceroute google.com
This identifies where delays occur—whether at your ISP, a regional hub, or the VPN tunnel. If delays appear only after connecting through a VPN, switching to another UFO VPN server usually helps.
Troubleshooting Ping Failures
When ping fails, it doesn’t always mean the internet is down. Here’s how to systematically approach it.
Basic Checks: Connectivity and Firewalls
- Ensure your device is connected to Wi-Fi or Ethernet.
- Temporarily disable firewalls or security apps.
- Restart your router/modem to refresh connectivity.
Pinging Reliable Servers like 8.8.8.8
Google’s DNS server 8.8.8.8 is a common test target because it’s almost always online.
- If you can ping 8.8.8.8 but not websites, the issue is likely DNS.
- In that case, switching DNS servers or using VPN DNS (like UFO VPN’s encrypted DNS) can solve the problem.
Resolving VPN-Related Ping Issues
VPNs add encryption layers, which can increase latency. To optimize with UFO VPN:
- Select a server closest to your location 🌍
- Use streaming-optimized or gaming servers for stable connections
- Try split tunneling to keep critical apps outside the VPN tunnel
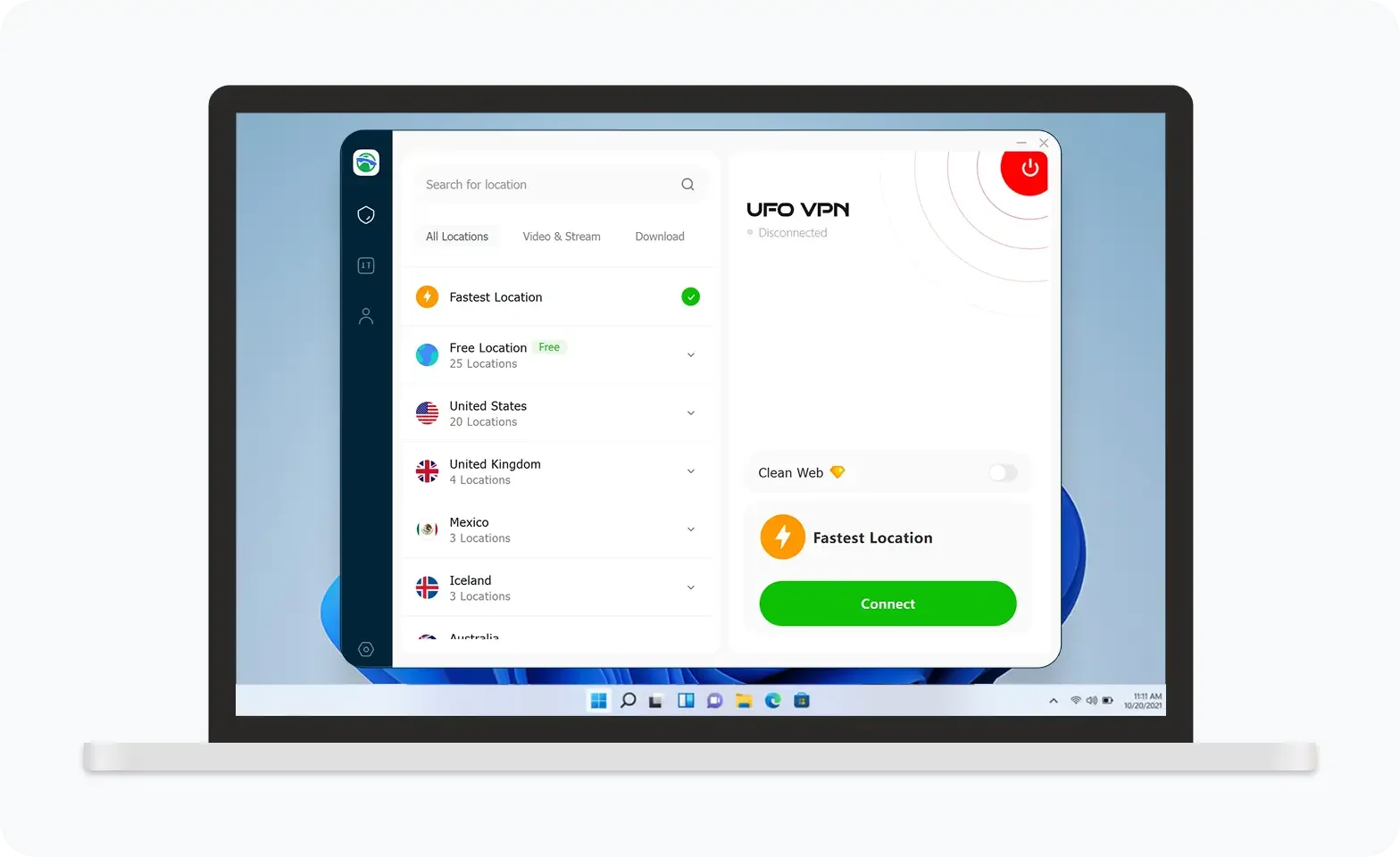
UFO VPN is an all-in-one VPN that offers unlimited access to 4D streaming like Netlfix, Disney Plus, no-ping gaming as PUBG, Roblox, CODM and social networking for YouTube, X, Facebook and more.
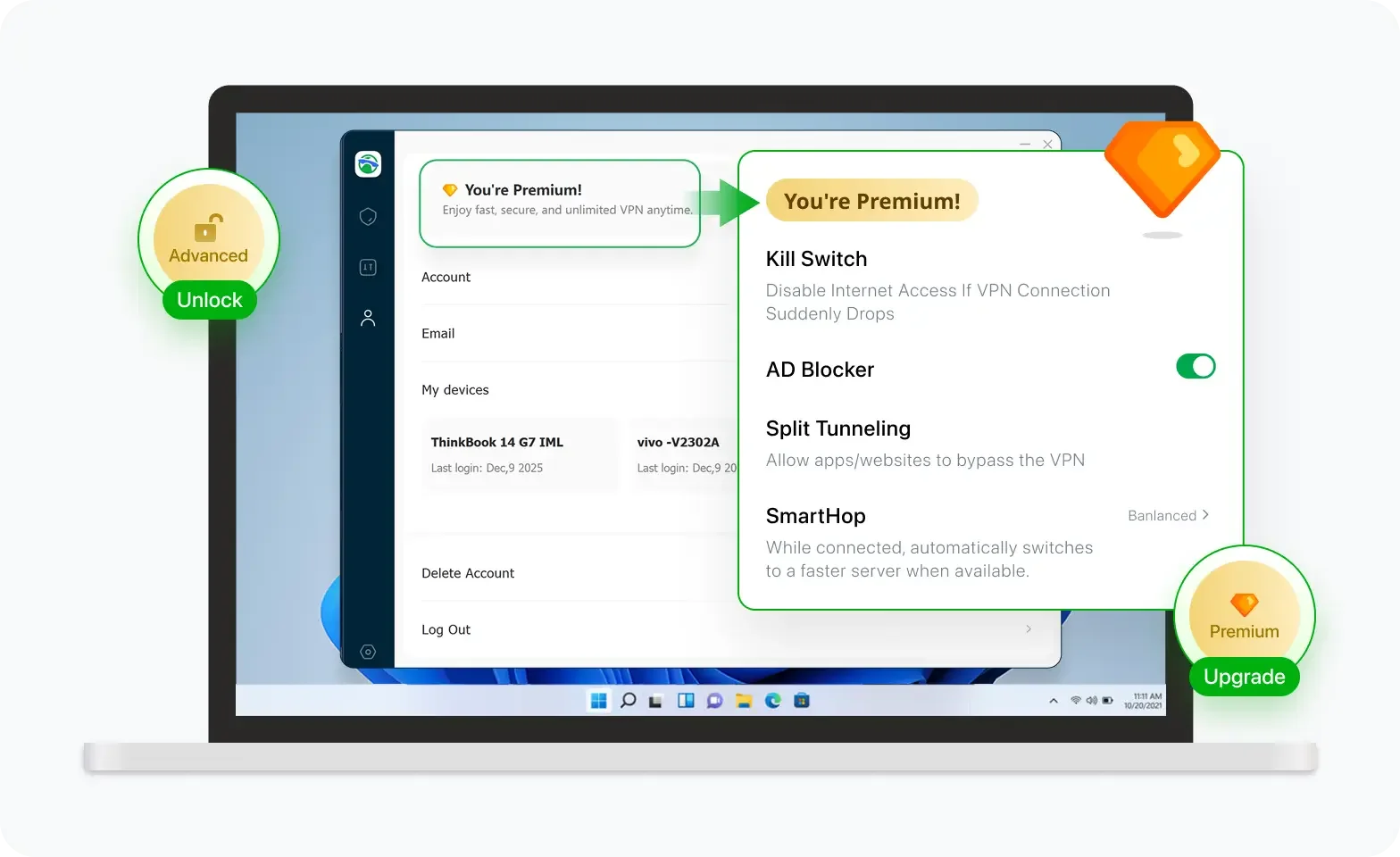
Unlock Pro Features
If you have upgraded to premium plan , feel free to enjoy premium servers for 4K streaming and advanced features like Kill Switch, Split Tunneling, and gaming acceleration. Your Mac is now fully optimized and protected. Inaddition to basic functions, we recommend you turn on

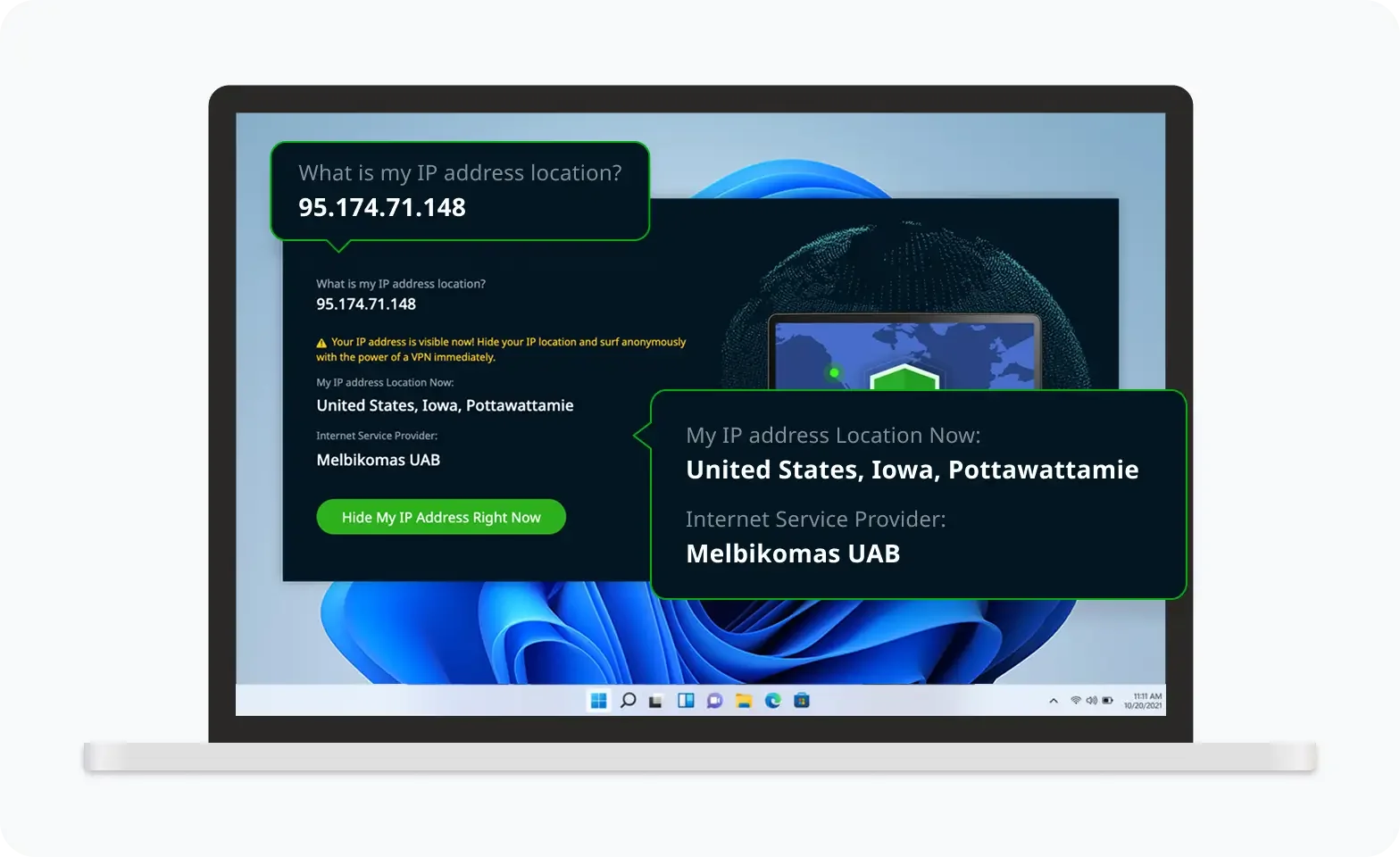
Verify Your IP Now
Use UFO VPN's " What is My IP " feature to see your new IP and location. This confirms your connection is secure, anonymous, and ready for safe browsing online anywhere at any time.

Conclusion
Ping is one of the simplest but most powerful tools in networking. In 2026, it remains just as relevant for checking connectivity, diagnosing lag, and troubleshooting VPN performance. By learning to interpret results and applying advanced techniques like traceroute, you’ll be well-equipped to keep your connection stable and secure. And if you combine ping diagnostics with tools like UFO VPN, you not only fix issues faster but also protect your privacy every time you connect. 🚀
FAQs
Can ping be blocked?
Yes, some networks or firewalls disable ICMP responses, so pinging won’t work.
What’s a “good” ping for gaming?
Under 50 ms is excellent; anything above 150 ms may cause noticeable lag.
Why do I get different ping results to the same server?
This can be due to network congestion, Wi-Fi instability, or VPN routing changes.
Can VPNs lower my ping?
Sometimes. If your ISP routes inefficiently, a VPN like UFO VPN can create a faster path.
What should I ping first when troubleshooting?
Start with your router (often 192.168.1.1), then external servers like 8.8.8.8.