What Can a VPN Do?
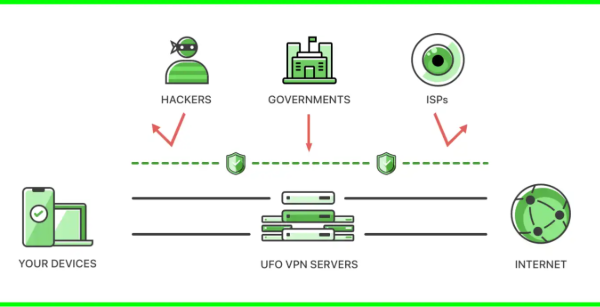
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) secures your internet traffic through encryption, hides your real IP address, and makes it possible to appear online as if you were browsing from another country.
This combination of privacy, anonymity, and unrestricted access is why people turn to VPNs like the free proxy VPN from UFO VPN for streaming, bypassing censorship, or staying safe on public Wi-Fi.
But not everyone can use a VPN. In some regions, VPN apps are blocked, while in workplaces or schools, they may be restricted. Others might find them too costly or worry about speed issues. That’s why many users look for VPN alternatives - tools that can cover at least part of what a VPN does. Let’s take a closer look at the most common options.
Best Alternatives to VPN (Free & Paid Options)
When you search for VPN alternatives or wonder what to use instead of VPNs, the choices can be overwhelming. Below are the most common technologies and tools people consider, with their pros, cons, and ideal use cases.
1. Proxy Servers (Mostly Free)
What it is: A proxy server acts as an intermediary between you and the internet. Your requests go through the proxy, which changes your IP address before reaching the website.
Pros:
-
Hides your IP, making it seem like you’re browsing from another region.
-
Easy to set up in browsers and apps.
-
Often free or very cheap.
Cons:
-
Most proxies don’t encrypt your data, leaving traffic exposed.
-
Less reliable for streaming platforms or bypassing strong restrictions.
Best for: Light anonymity, basic access to region-restricted sites, or when you just need a quick workaround.
2. Smart DNS (Mostly Paid)
What it is: Smart DNS changes how your DNS requests are routed, helping you access content blocked by location without altering your IP.
Pros:
-
Works well for streaming (Netflix, Hulu, BBC iPlayer, etc.).
-
Faster than VPNs since no encryption overhead.
-
Can be used on devices that don’t support VPNs, like smart TVs.
Cons:
-
No encryption, meaning your ISP can still track your activity.
-
Doesn’t protect you on public Wi-Fi.
Best for: Media streaming and bypassing geo-blocks when privacy isn’t your main concern.
3. SSH Tunneling (Free if Self-Hosted, Paid for Third-Party Services)
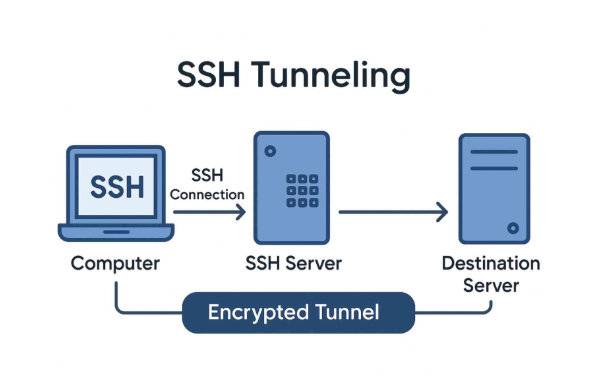
What it is: An encrypted tunnel using the Secure Shell (SSH) protocol, commonly used for secure connections to servers.
Pros:
-
Strong encryption for specific connections.
-
Useful for developers or IT professionals.
Cons:
-
Complex setup compared to VPNs.
-
Typically, it only secures specific applications, not all traffic.
Best for: Tech-savvy users who need secure server connections but don’t want a full VPN.
4. Tor (The Onion Router) (Free)
What it is: A network that routes your traffic through multiple nodes, encrypting it at each step.
Pros:
-
Extremely private and anonymous.
-
Free to use.
Cons:
-
Very slow compared to VPNs.
-
Some websites block Tor traffic.
-
Not ideal for streaming or downloads.
Best for: Journalists, activists, or anyone needing maximum anonymity over speed.
5. Shadowsocks (Free/Open-Source, Paid if Using VPS Services)
What it is: An open-source, proxy-based protocol designed to bypass censorship. Multiple client and server implementations exist, making it a flexible tool for regions with strict internet controls.
Pros:
-
Lightweight and fast compared to VPNs.
-
Strong at bypassing deep packet inspection (DPI).
-
Customizable encryption methods for added security.
Cons:
-
Requires manual setup and technical knowledge.
-
Only proxies selected traffic, not full-device encryption.
-
Security depends on proper configuration.
Best for: Users in heavily censored regions who need fast, reliable, and customizable access to restricted websites.
6. Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) (Paid)
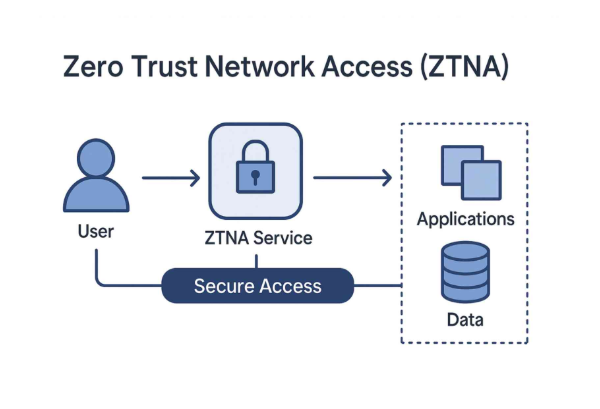
What it is: A security model based on “never trust, always verify.” Access is granted only to specific apps and resources after continuous authentication.
Pros:
-
Highly secure for organizations.
-
Reduces risks of lateral attacks inside networks.
Cons:
-
Complex to implement.
-
Mainly designed for businesses, not individuals.
Best for: Companies with remote teams needing strict, scalable security.
7. Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) (Paid)
What it is: A framework combining networking and security (like ZTNA, firewalls, secure web gateways) into a cloud-based service.
Pros:
-
All-in-one security solution.
-
Cloud-native and scalable.
Cons:
-
Expensive and requires technical expertise.
-
Not practical for individuals.
Best for: Large enterprises shifting to cloud infrastructure.
8. SD-WAN (Software-Defined Wide Area Network) (Paid)
What it is: A virtual WAN architecture that optimizes network traffic across multiple connections.
Pros:
-
Improves application performance.
-
Can include built-in encryption.
Cons:
-
Primarily for enterprise use.
-
Expensive and complex to manage.
Best for: Organizations with global offices needing secure, optimized traffic routing.
Are VPN Replacements Really Better Than VPNs?
While these VPN replacements each serve a purpose, the question remains: are they truly better than a VPN?
-
For individuals: Most alternatives either lack encryption (proxies, Smart DNS) or sacrifice speed (Tor). A well-designed VPN like UFO VPN balances speed, encryption, and usability - making it the most practical choice for everyday privacy, streaming, and browsing.
-
For businesses: Advanced frameworks like ZTNA and SASE are excellent, but they are complex and costly. For small and medium businesses, VPNs still provide a cost-effective balance between simplicity and security.
In short, alternatives can complement or specialize where VPNs fall short, but few can fully replace them.
FAQs
1. What is the best alternative to a VPN?
It depends on your needs. For streaming, Smart DNS is fast. For anonymity, Tor works best. For business security, ZTNA or SASE are leading options.
2. Is there a free VPN alternative?
Yes, Tor and some proxy services are free. However, free tools often come with slower speeds, limited features, or privacy concerns.
3. Can Smart DNS replace a VPN?
No. Smart DNS is great for unblocking websites, but it doesn’t encrypt your traffic. It’s not a full replacement if you value privacy.
4. What technology will replace VPN for businesses?
Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) and Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) are considered the future replacements for enterprise VPNs.
5. Is Tor safer than a VPN?
Tor provides more anonymity, but VPNs are faster and more reliable for daily use. Many users even combine them for extra privacy.
Conclusion
Exploring VPN alternatives reveals many options, from proxies and Smart DNS to enterprise solutions like ZTNA and SASE. While each has its strengths, most cannot fully replace the balance of security, privacy, and usability that a VPN provides. For everyday use, a VPN—especially reliable services like UFO VPN—remains the most practical choice, with alternatives serving as useful complements depending on your needs.