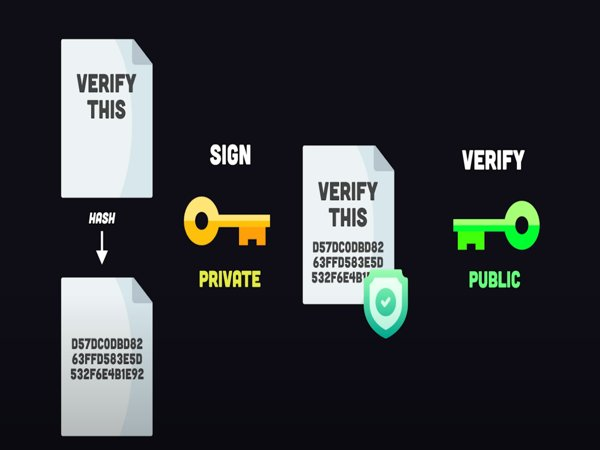
Cryptography Explained: The Core Concept
At its essence, cryptography is the art and science of securing information. It involves techniques that convert readable data, called plaintext, into scrambled, unreadable data, known as ciphertext. Only authorized parties with the correct key can decrypt the information back into a readable form.
In practical terms, cryptography ensures three key principles:
- Confidentiality – Unauthorized users cannot read your data.
- Integrity – Data cannot be altered without detection.
- Authentication – Parties can verify the origin of data.
Cryptography isn’t just for governments or large corporations; it’s embedded in everyday tools, from messaging apps to financial platforms.
Types of Cryptography
Modern cryptography can be broadly divided into several types, each serving specific purposes:
| Type | Description |
Common Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Symmetric-key | Same key for encryption and decryption | File encryption, VPNs, local storage |
| Asymmetric-key | Uses public/private key pairs | Email encryption, blockchain transactions |
| Hash functions | One-way functions to verify data integrity |
Password storage, digital signatures |
| Post-quantum | Algorithms resistant to quantum attacks |
Emerging security standards, Web3 applications |
The choice of cryptographic method depends on the context. For instance, VPNs like UFO VPN often use symmetric encryption for speed and efficiency, ensuring secure internet browsing for users without compromising performance.
Everyday Uses of Cryptography
Cryptography isn’t just a theoretical concept—it powers many of the tools we rely on daily.
Secure Messaging Apps
Apps like Signal, WhatsApp, and Telegram rely on end-to-end encryption, a cryptographic method ensuring that only the sender and recipient can read the messages. Without encryption, even service providers could potentially access your private conversations.
Combining encrypted messaging with a VPN such as UFO VPN adds another privacy layer, masking your IP address so that even metadata about your communication remains harder to track.
Online Payments & Banking
Every time you use your credit card online, cryptography works behind the scenes. SSL/TLS protocols encrypt the connection between your browser and the bank’s servers, preventing attackers from intercepting sensitive information.
Additionally, tools like UFO VPN provide extra protection when using public Wi-Fi, ensuring that financial transactions remain private even on unsecured networks.
Benefits and Limitations of Cryptography
Cryptography offers undeniable advantages:
- Data security: Protects sensitive information from unauthorized access.
- Trust: Digital signatures authenticate identities online.
- Compliance: Meets regulatory requirements for data protection.
However, it also has limitations:
- Key management: Losing encryption keys can mean permanent data loss.
- Performance overhead: Strong encryption can slow down applications.
- Quantum threats: Future quantum computers may break traditional encryption methods.
Despite these limitations, combining strong cryptographic protocols with privacy tools like UFO VPN ensures a more robust defense against current and emerging threats.
Cryptography vs. Encryption: What’s the Difference?
While often used interchangeably, cryptography and encryption are not identical:
- Cryptography: The broader field encompassing all methods to secure information, including hashing, digital signatures, and encryption.
- Encryption: A subset of cryptography focused specifically on converting data into unreadable formats.
Think of cryptography as the “science” and encryption as one of its key “tools.” In daily practice, using encrypted websites (HTTPS) and secure communication channels ensures cryptographic principles are actively protecting your data.
The Future of Cryptography
With technology evolving rapidly, cryptography is also advancing.
Quantum Computing and Post-Quantum Algorithms
Quantum computers could theoretically break many of today’s encryption methods. Post-quantum cryptography is being developed to withstand these attacks, ensuring long-term data security for sensitive information and blockchain-based systems.
Zero-Knowledge Proofs and Web3
Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZKPs) allow one party to prove knowledge of data without revealing it. This concept is increasingly used in Web3 applications and decentralized finance (DeFi), enhancing privacy and reducing the risk of data leakage.
How to Stay Secure in Daily Life
Understanding cryptography is just the first step; applying practical security measures is equally important. Even the strongest encryption can’t protect you if basic online hygiene is ignored.
Always Use HTTPS Websites
HTTPS encrypts data transmitted between your browser and websites, preventing eavesdroppers from intercepting sensitive information such as passwords, payment details, or personal messages. Always look for the padlock icon in the browser address bar before entering any confidential information. Additionally, avoid clicking links from unknown sources or email attachments, as attackers often use phishing sites that mimic legitimate HTTPS websites. For enhanced protection, consider using a VPN like UFO VPN, which encrypts your traffic and masks your IP, making it harder for attackers to track your online activity.
Use Strong Passwords and a Password Manager
Weak or reused passwords remain one of the biggest security risks. To protect yourself:
- Create strong, unique passwords for every account using a combination of letters, numbers, and symbols.
- Use a password manager to securely store and generate complex passwords, reducing the need to remember dozens of credentials.
- Enable two-factor authentication (2FA) wherever possible to add an extra verification step.
Combining these practices with a VPN like UFO VPN enhances your security by encrypting your internet connection, hiding your IP address, and protecting your data even on public or untrusted networks. This approach ensures that even if a password is compromised, attackers cannot easily trace or intercept your activity.
By following these steps consistently, users can significantly reduce the risk of cyberattacks, maintain their privacy, and enjoy a safer online experience across all devices.
UFO VPN is an all-in-one VPN that offers unlimited access to 4D streaming like Netlfix, Disney Plus, no-ping gaming as PUBG, Roblox, CODM and social networking for YouTube, X, Facebook and more.
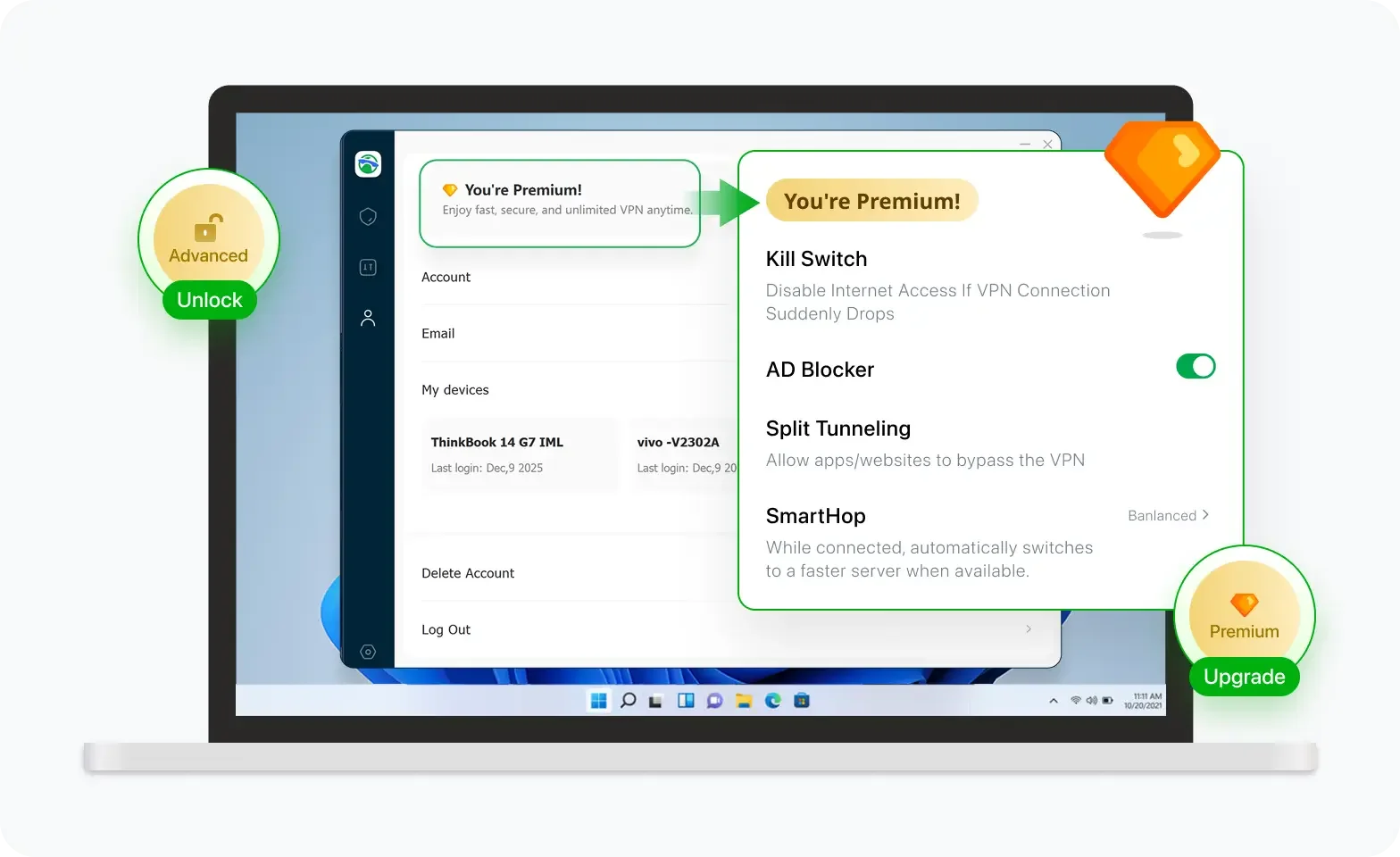
Unlock Pro Features
If you have upgraded to premium plan , feel free to enjoy premium servers for 4K streaming and advanced features like Kill Switch, Split Tunneling, and gaming acceleration. Your Mac is now fully optimized and protected. Inaddition to basic functions, we recommend you turn on

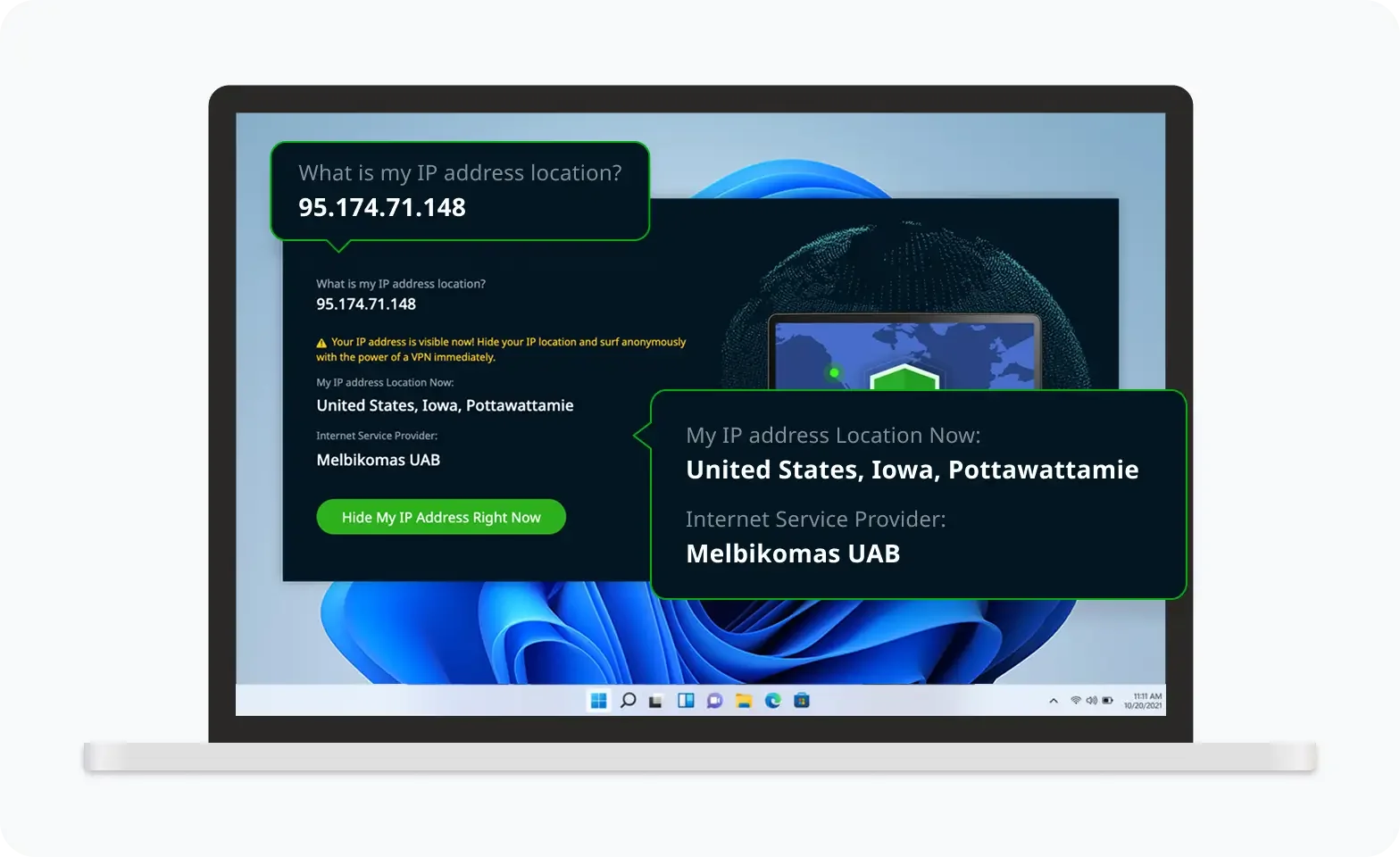
Verify Your IP Now
Use UFO VPN's " What is My IP " feature to see your new IP and location. This confirms your connection is secure, anonymous, and ready for safe browsing online anywhere at any time.

Conclusion
Cryptography is the backbone of digital security in 2026, powering secure messaging, financial transactions, and emerging Web3 technologies. While it offers robust protection, combining cryptographic best practices with tools like UFO VPN maximizes privacy and security, shielding you from potential cyber threats.
By understanding cryptography, using encryption wisely, and adopting practical measures like strong passwords and VPNs, individuals and businesses can stay safe in an increasingly interconnected digital world. 🔐🌐
FAQs
Is VPN necessary if websites use HTTPS?
While HTTPS encrypts data between your browser and website, a VPN like UFO VPN hides your IP address and encrypts all internet traffic, adding extra privacy.
Can quantum computers break current encryption?
Yes, theoretically. Post-quantum cryptography is being developed to prevent future quantum attacks.
What’s the difference between symmetric and asymmetric encryption?
Symmetric uses a single key for encryption/decryption, while asymmetric uses a public/private key pair.
How do zero-knowledge proofs enhance privacy?
They allow verification without revealing the underlying data, reducing exposure in online transactions.
Are password managers safe?
Yes, especially when combined with strong master passwords and VPN protection.