What is bcrypt

At its core, what is bcrypt? It’s a time-tested password hashing algorithm built on a variant of the Blowfish cipher. Unlike encryption (which is reversible with a key), hashing is one-way—there’s no secret that can “decrypt” a hash back into the original password. Instead, when you sign in, the site runs bcrypt hashing on the password you typed and compares the result against the stored hash.
Key properties that make bcrypt a smart default:
-
Salted by design: Every hash includes a unique, random salt (typically 128-bit). Salts make identical passwords produce different hashes and defeat rainbow tables.
-
Configurable work factor (“cost”): Bcrypt lets sites dial up the computational cost, slowing down attackers who try billions of guesses per second.
-
Battle-tested: It’s been widely deployed for decades in frameworks and identity providers, making “what is bcrypt” not just theory but proven practice.
When you see a stored password string beginning with $2a$, $2b$, or $2y$ (commonly $2b$), that’s a bcrypt hash containing the version, cost, salt, and hash—all in about 60 characters.
How bcrypt hashing works

You don’t need to be a cryptographer to understand bcrypt hashing mechanics well enough to make good decisions.
-
Generate a salt
-
For each password, the system generates a random salt and stores it alongside the hash (bcrypt embeds it inside the hash string itself).
-
-
Choose a cost factor
-
The cost (also called work factor) determines how many internal rounds bcrypt performs—roughly
2^cost. A cost of 12 is common; higher costs increase security and CPU time.
-
-
Hash the password + salt
-
Bcrypt runs a computationally expensive key setup over the salt and password and outputs a fixed-length result.
-
-
Store the hash string
-
The database saves a self-contained string: version + cost + salt + hash. No plaintext password is stored—ever.
-
-
Verification
-
On login, the site extracts the cost and salt from the stored hash and runs bcrypt hashing again on your candidate password. If the results match, you’re in.
-
Because the cost is tunable, organizations can increase it over time as hardware gets faster—keeping “guessing per second” expensive for attackers. That adaptability is a huge part of answering what is bcrypt and why it’s still relevant.
Why bcrypt remains a strong password hashing algorithm
If your question is what is bcrypt and “is it still secure,” the answer is yes—when configured properly.
-
Slow by design: Attackers thrive on speed. Bcrypt’s cost setting throttles brute-force and dictionary attacks.
-
Unique per user: Built-in salts ensure the same password in two accounts won’t share a hash.
-
Framework support: Most modern frameworks provide safe bcrypt wrappers, reducing developer mistakes.
-
Migration path: Because the cost lives in the hash, you can “re-hash” users at a higher cost transparently upon next login.
Limits to keep in mind:
-
GPU resistance vs. memory hardness: Bcrypt is compute-hard but not memory-hard, which brings us to bcrypt vs Argon2 and others.
-
Bad passwords remain bad: No password hashing algorithm can rescue “123456.” Strong, unique passphrases still matter.
When people ask what is bcrypt, they usually want to confirm that their platform uses a slow, salted function with a modern cost. Bcrypt checks those boxes.
Bcrypt vs Argon2, PBKDF2, and scrypt

Comparing algorithms helps clarify what is bcrypt relative to newer options.
-
Argon2 (Argon2id recommended): Winner of the Password Hashing Competition. It’s memory-hard, meaning it consumes RAM to slow down GPU/ASIC cracking. Great modern default when your platform supports it.
-
scrypt: Also memory-hard and widely available, but less commonly the first choice than Argon2 today.
-
PBKDF2: Very mature and standardized, but primarily CPU-bound (not memory-hard). Often used where FIPS or specific compliance regimes apply.
-
Bcrypt: Extremely well-supported, cost-tunable, and still secure in practice. Lacks intrinsic memory hardness but remains a strong password hashing algorithm for many stacks.
If you’re building new systems with modern libraries, Argon2id is an excellent default. If you’re on a mature platform with first-class bcrypt support, bcrypt at an appropriate cost remains a safe, pragmatic choice. That’s the nuance behind bcrypt vs Argon2—both can be right, depending on your constraints.
Implementing bcrypt correctly

A correct setup turns “what is bcrypt” from a concept into concrete protection.
-
Use trusted libraries. Avoid hand-rolling. Pick well-maintained packages for your language/framework.
-
Pick a sensible cost. Benchmark on your production hardware. Aim for ~100–250 ms per hash on your login path; increase over time.
-
Unique salt per hash. Don’t reuse salts or invent patterns; good libraries do this automatically.
-
Pepper (optional). Some teams add a server-side secret (“pepper”) stored outside the database. It’s not a silver bullet, but it adds a hurdle if the DB alone leaks.
-
Re-hash on login. If cost increases, transparently re-hash the user’s password at next successful login.
-
Lockout & rate limiting. Throttle repeated failures and add bot detection; bcrypt slows offline attacks, not online guessing.
-
Full pipeline security. Use TLS everywhere, secure password reset flows, and protect databases and logs (hashes must never appear in logs).
If you’re auditing a vendor, ask directly: “Do you store hashed passwords using bcrypt hashing (or Argon2id) with unique per-user salts and an adjustable cost?” That one sentence captures the heart of what is bcrypt in practice.
What users can do today ?
You don’t control a site’s backend, but you do control your inputs and environment. Here’s how to apply the spirit of what is bcrypt as a user:
-
Use a password manager to generate long, unique passphrases (e.g., 16–24 characters). Strong inputs make any password hashing algorithm more effective.
-
Turn on multi-factor authentication (MFA)—prefer app codes or security keys. Hashing protects stored passwords; MFA protects live sessions.
-
Unique everywhere. If one service leaks, unique passwords stop reuse attacks on your other accounts.
-
Update breached passwords fast. When notified of a breach, change the password immediately and anywhere you reused it (ideally, you never did).
-
Protect the route with a VPN on public Wi-Fi. Before signing in at cafés, hotels, airports, open free proxy VPN in UFO VPN and connect to the nearest location. A VPN encrypts your traffic and masks your IP from venue operators. It doesn’t replace bcrypt hashing on the server—but it prevents eavesdroppers and sketchy hotspots from seeing your credentials in transit (alongside TLS).
-
Beware phishing. The strongest hash won’t help if you hand your password to a fake page. Check URLs carefully and use a manager’s auto-fill (it won’t fill on impostor domains).
💛4 Steps Open UFO VPN💛
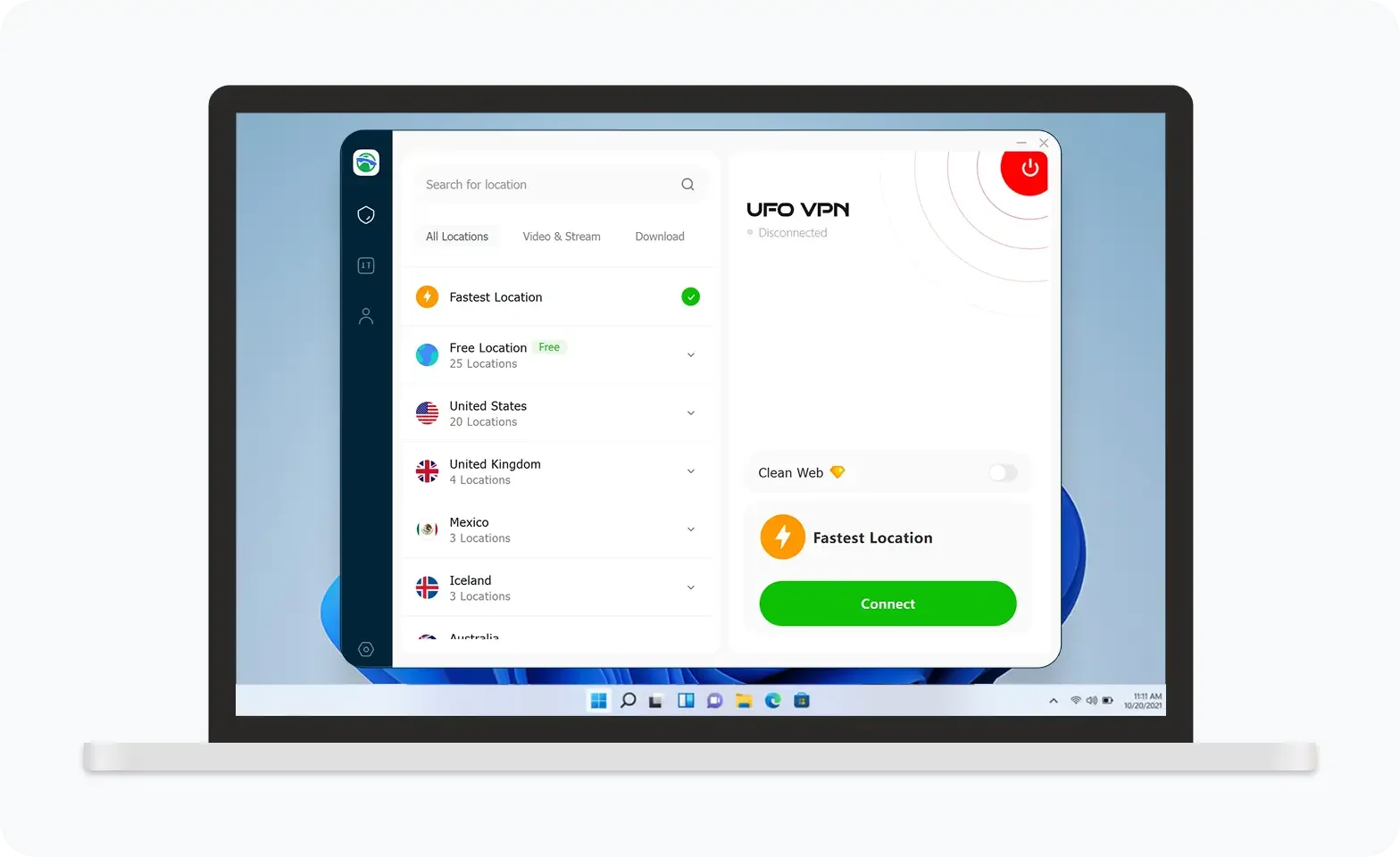
UFO VPN is an all-in-one VPN that offers unlimited access to 4D streaming like Netlfix, Disney Plus, no-ping gaming as PUBG, Roblox, CODM and social networking for YouTube, X, Facebook and more.
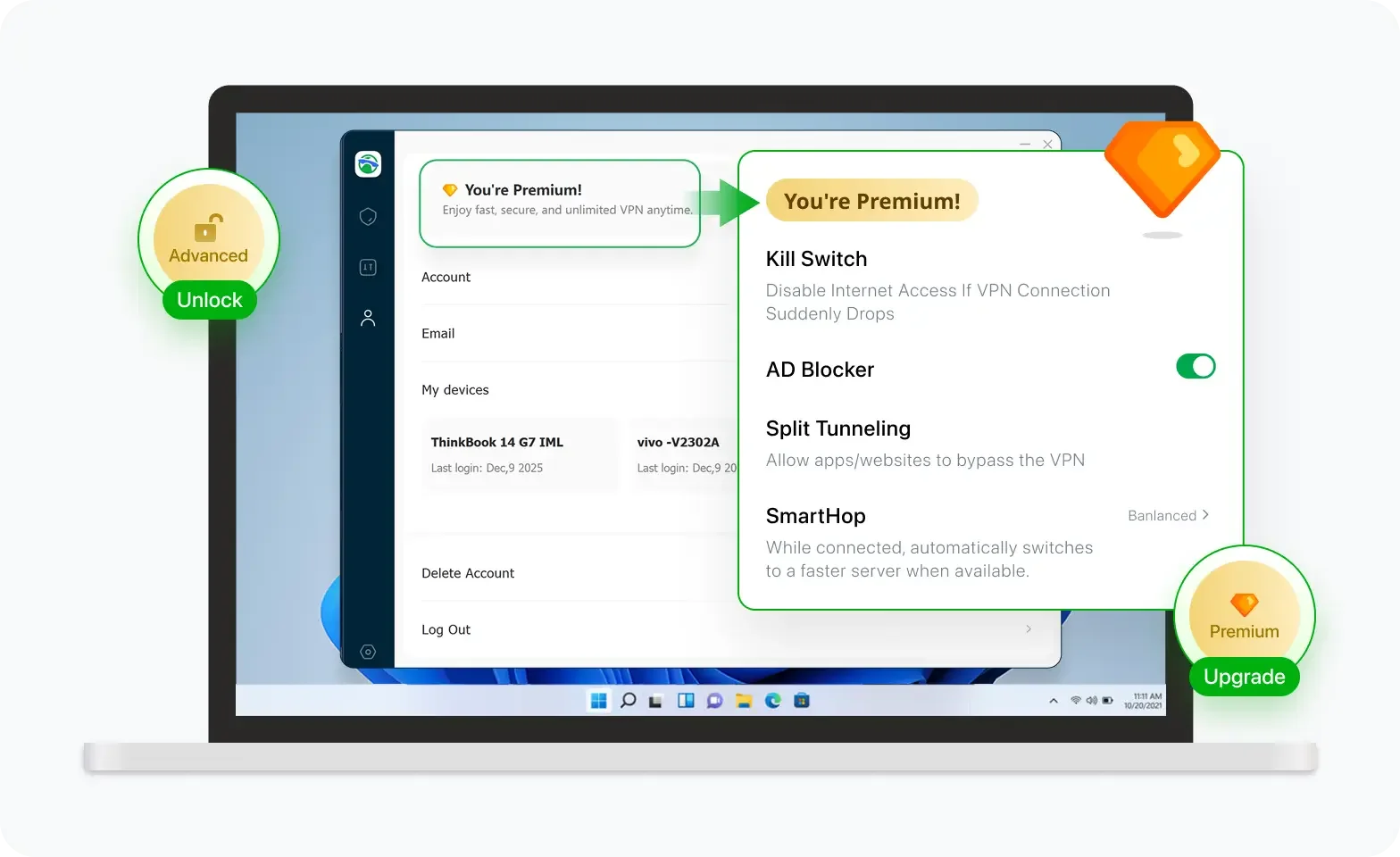
Unlock Pro Features
If you have upgraded to premium plan , feel free to enjoy premium servers for 4K streaming and advanced features like Kill Switch, Split Tunneling, and gaming acceleration. Your Mac is now fully optimized and protected. Inaddition to basic functions, we recommend you turn on

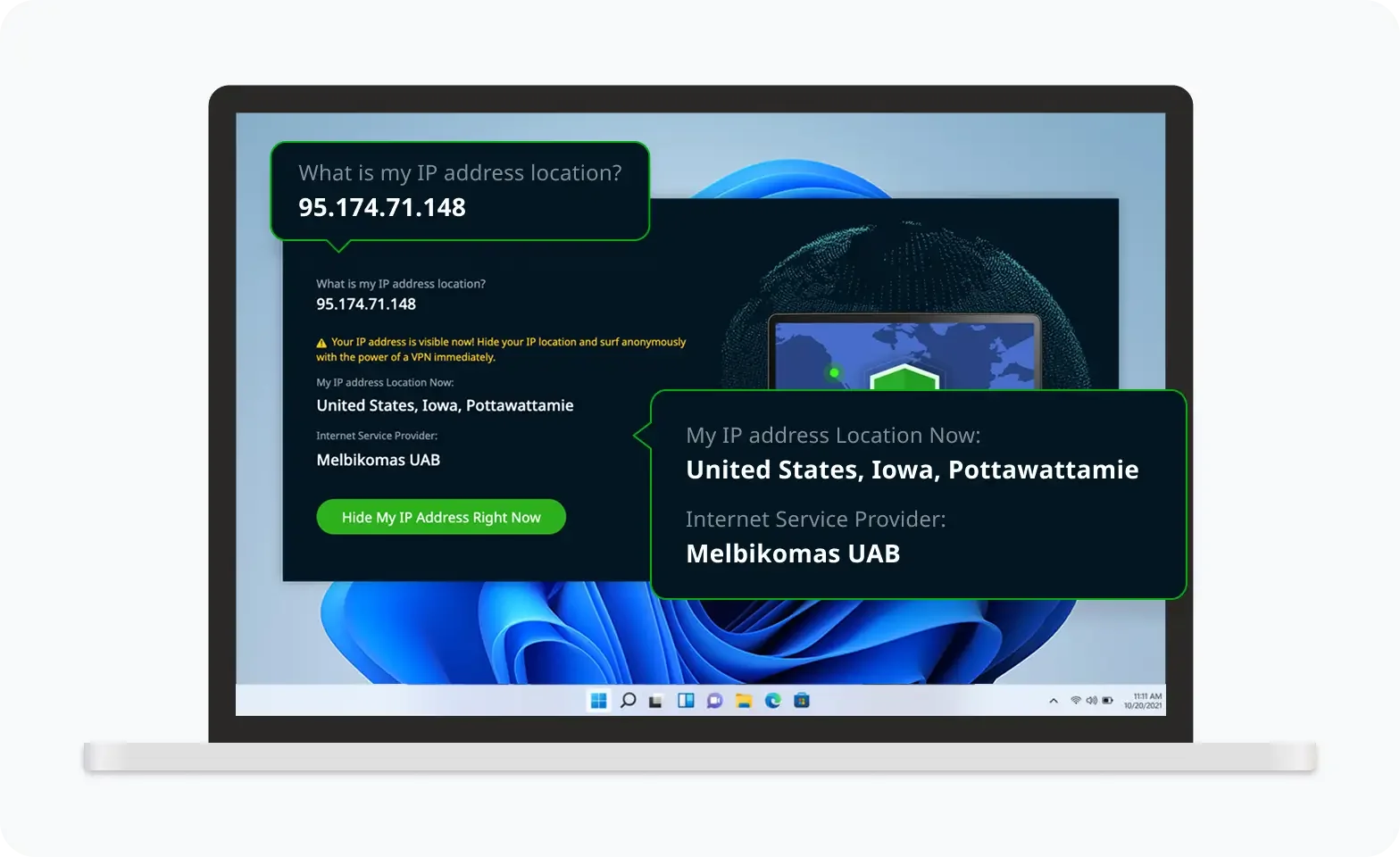
Verify Your IP Now
Use UFO VPN's " What is My IP " feature to see your new IP and location. This confirms your connection is secure, anonymous, and ready for safe browsing online anywhere at any time.

These habits pair with server-side bcrypt hashing to form defense-in-depth.
Spotting good practices on sites you use
You can’t easily see the hash algorithm a service uses, but some signals indicate mature handling:
-
Modern authentication flows: Support for passkeys or security keys usually correlates with solid password storage.
-
Transparent security pages: Providers that publish details (e.g., “we use bcrypt hashing with per-user salts”) earn trust.
-
Responsible disclosure & bug bounty: A program for security researchers suggests the team invests in hardening.
-
Breached-password checks: Services that prevent known-breached passwords demonstrate care beyond the bare minimum.
If a provider is vague, ask support. The very question—what is bcrypt and do you use it?—encourages better disclosure.
FAQs
What is bcrypt in one sentence?
A slow, salted password hashing algorithm that turns your password into a one-way, cost-tunable hash, making large-scale guessing attacks much harder.
Is bcrypt still safe?
Yes—configured with unique salts and an appropriate cost, bcrypt remains secure and widely recommended. For new builds, Argon2id is also an excellent choice.
Bcrypt vs Argon2: which should my team use?
If your stack supports Argon2id easily, use it for memory-hard resistance to GPUs/ASICs. If not, bcrypt with a modern cost is still strong and battle-tested.
Can a hacker reverse a bcrypt hash?
Not directly. Attackers attempt guesses and hash them until they find a match. Bcrypt’s cost setting makes each guess slow, reducing feasibility.
What does the bcrypt “cost” number mean?
It controls work—roughly 2^cost iterations. Higher cost = more CPU time per hash. Teams pick a cost that’s safe yet performant for logins.