Defining Big Tech: Scope and Characteristics

Core Players
When we talk about big tech, we typically refer to a handful of multinational corporations that dominate key segments of the digital economy. These include:
-
Google (Alphabet Inc.) – Leader in search, online advertising, and mobile operating systems.
-
Apple – Pioneer in smartphones, tablets, and digital ecosystems.
-
Meta Platforms (Facebook) – Major player in social networking, virtual reality, and advertising.
-
Amazon – E-commerce giant and cloud computing powerhouse (AWS).
-
Microsoft – Software behemoth with a strong presence in operating systems, productivity software, and cloud services.
Together, these firms control vast amounts of data, influence user behavior, and set many of the standards for digital services worldwide.
Key Characteristics
-
Network Effects: Platforms grow more valuable as more users join (e.g., social networks, marketplaces).
-
Data-Driven Insights: Extensive data collection fuels personalized services and targeted advertising.
-
Economies of Scale: Massive infrastructure investments lower marginal costs and erect high barriers to entry.
-
Vertical Integration: Control over hardware, software, and services creates cohesive ecosystems (e.g., Apple’s iOS and App Store).
The Evolution of Big Tech

Early Beginnings
-
1970s–1990s: Foundations laid by hardware and enterprise software companies (Microsoft, IBM).
-
Late 1990s–2000s: The dot-com era brought internet-centric models (Amazon, Google).
-
2010s: Rise of smartphones and social media cemented Meta and Apple’s dominance.
Recent Developments
-
Cloud Migration: AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud now form the backbone of many businesses.
-
AI & Machine Learning: Investments in generative AI, voice assistants, and autonomous systems.
-
Metaverse & VR/AR: Meta’s rebranding effort highlights the shift toward immersive digital experiences.
Economic and Social Impacts

Economic Dominance
-
Market Capitalization: Combined valuations exceed several trillion dollars.
-
Job Creation: Millions employed directly or indirectly through developer ecosystems and service partners.
-
Mergers & Acquisitions: Frequent acquisitions of promising startups to neutralize competition and acquire talent.
Social Influence
-
Information Dissemination: Platforms like Facebook and YouTube shape public opinion—for better or worse.
-
Digital Divide: While services expand global access, disparities in connectivity and digital literacy persist.
-
Cultural Trends: Viral challenges, memes, and influencer culture emerge from big tech platforms.
Privacy Concerns and Data Practices
Data Collection Practices
-
User Tracking: Cookies, device fingerprinting, and behavioral analytics follow users across the web.
-
Personal Profiles: Aggregated data builds detailed profiles used for personalized ads.
Risks to Individual Privacy
-
Surveillance Capitalism: Monetizing personal information without transparent user consent.
-
Data Breaches: Massive troves of personal data vulnerable to cyberattacks.
-
Algorithmic Bias: Automated systems may perpetuate or exacerbate societal biases.
The Future of Big Tech

Emerging Trends
-
Decentralization: Blockchain and Web3 aim to redistribute power away from centralized platforms.
-
AI Regulation: Governments debating frameworks to govern AI development and deployment.
-
Sustainability: Pressure on data centers to reduce carbon footprints and improve energy efficiency.
Potential Challenges
-
Competition: New entrants and niche players could erode big tech’s market share.
-
Public Trust: Privacy scandals and misinformation crises may undermine user confidence.
-
Geopolitical Tensions: Tech supply chain disruptions and national security concerns.
Why You Need a VPN in the Age of Big Tech

Amidst the vast reach of big tech platforms, safeguarding your online activities is more critical than ever. Here’s how Best free VPN can help:
-
Traffic Encryption: Shield your browsing and communication from prying eyes—whether hackers, ISPs, or data brokers.
-
Anonymity: Mask your IP address and prevent big tech platforms from pinpointing your exact location.
-
Bypass Throttling: Avoid ISP slowdowns when streaming, gaming, or downloading large files.
-
Access Global Content: Connect to servers worldwide to experience services as if you were in another country.
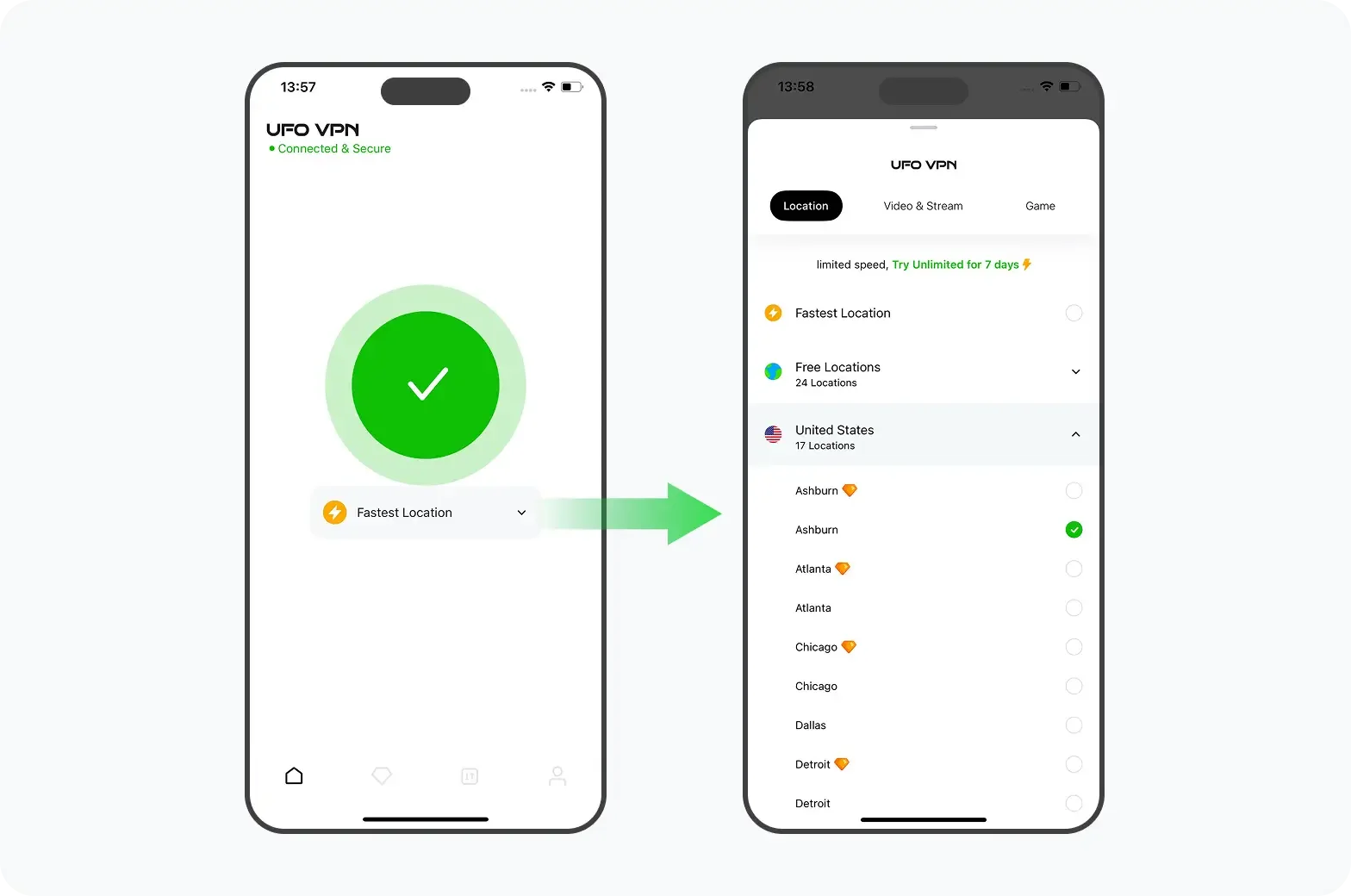
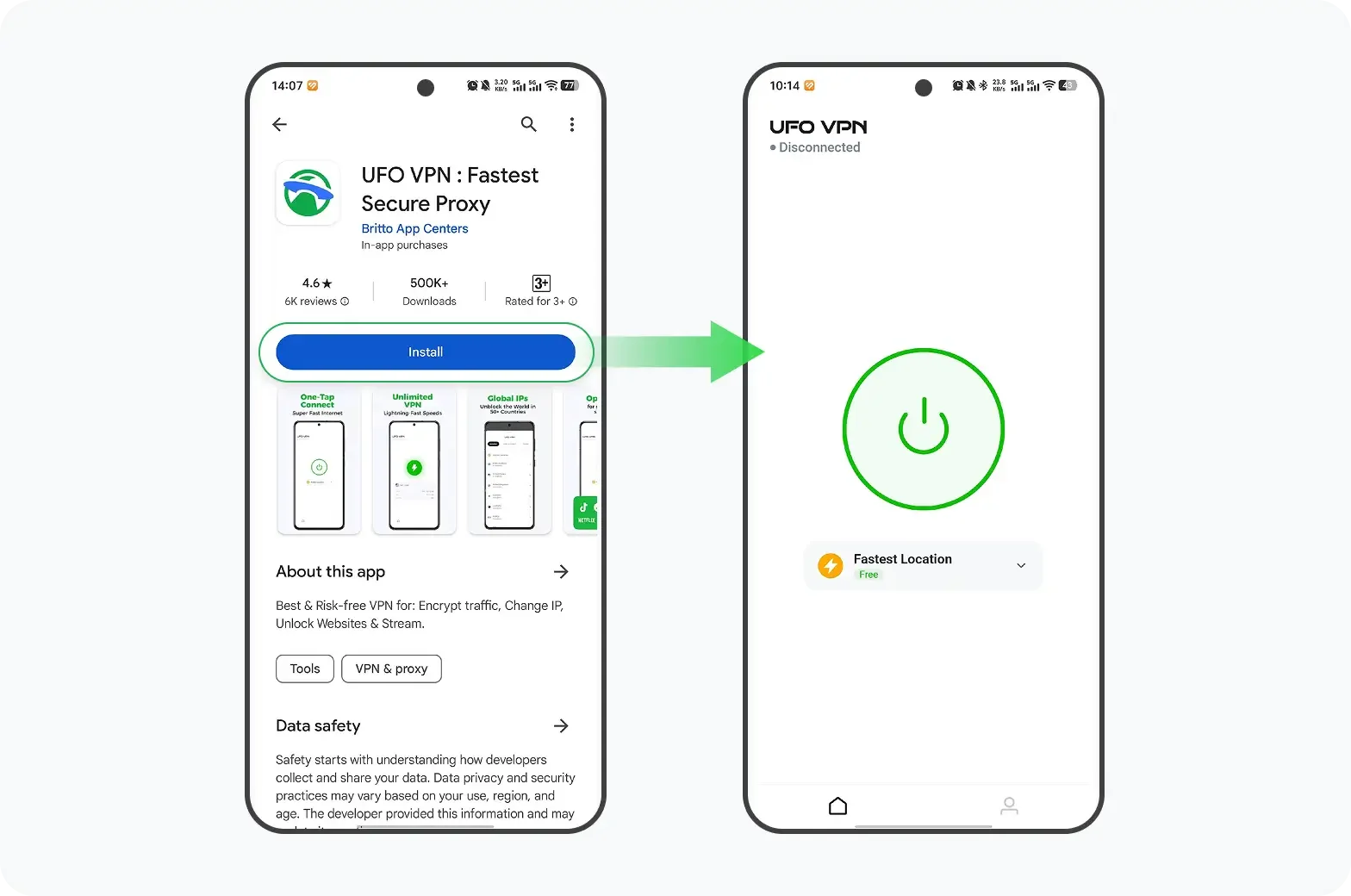
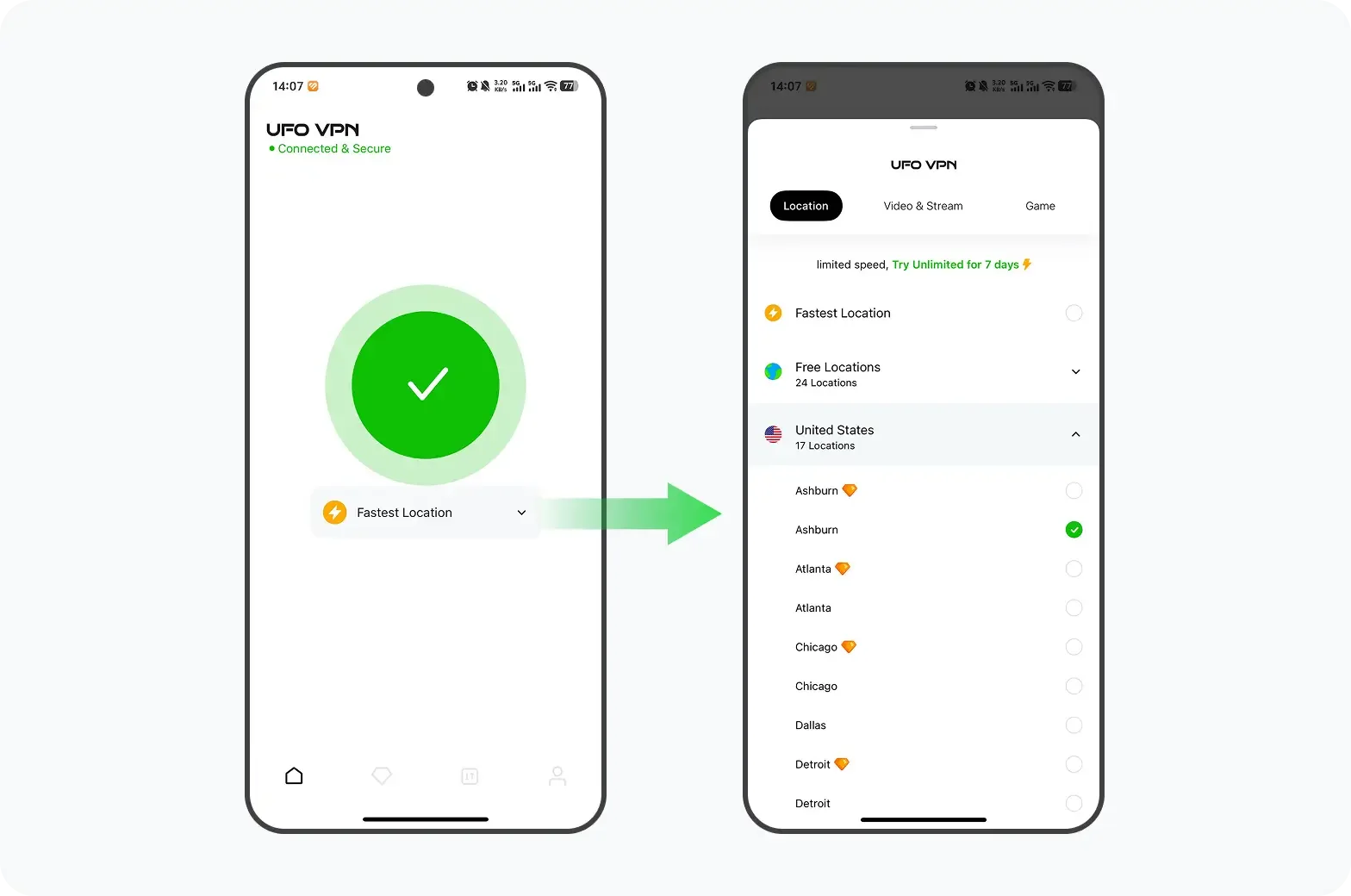
How to get a free and safe VPN
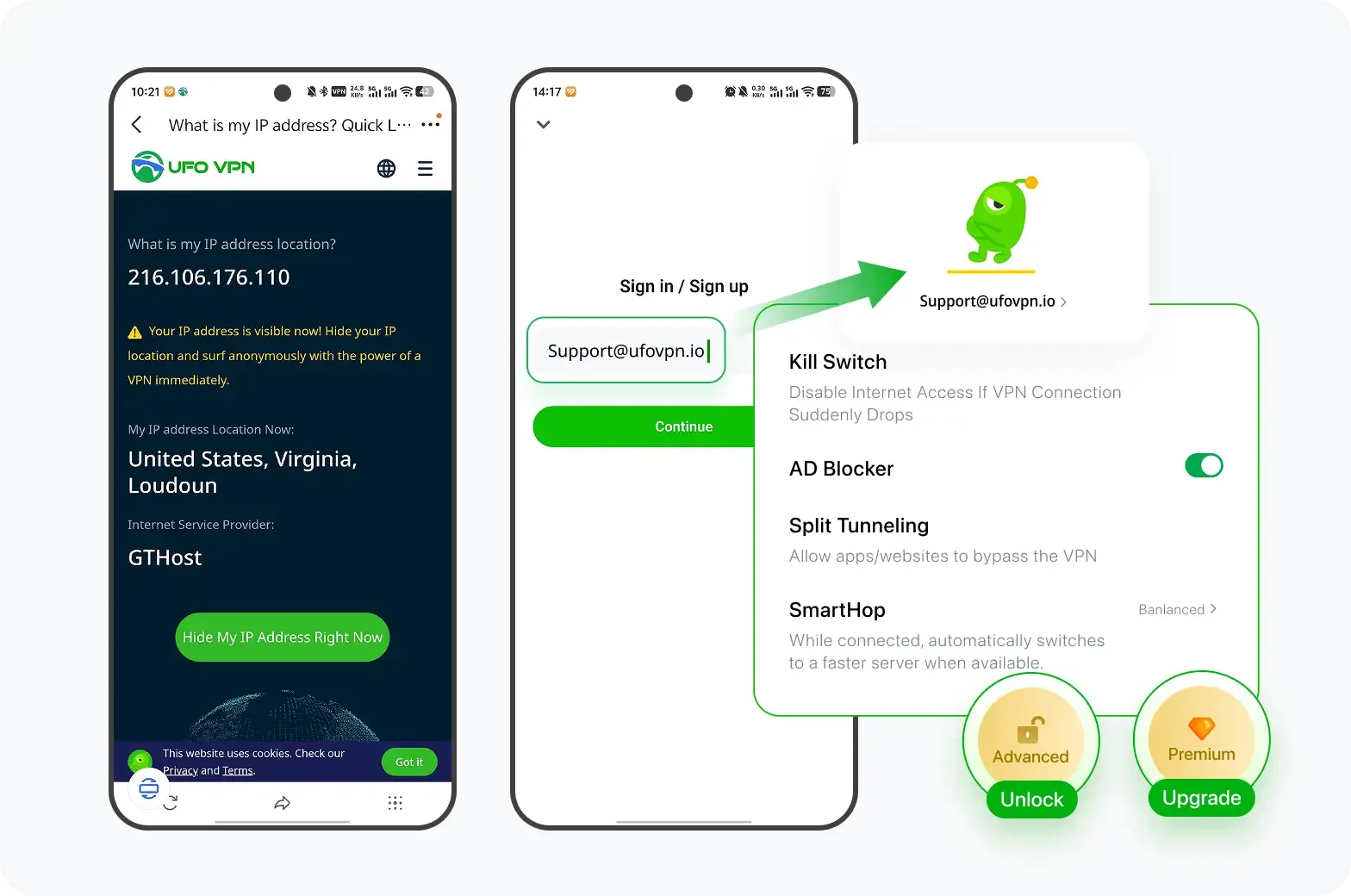
UFO VPN is an all-in-one VPN that offers unlimited access to 4D streaming like Netlfix, Disney Plus, no-ping gaming as PUBG, Roblox, CODM and social networking for YouTube, X, Facebook and more.
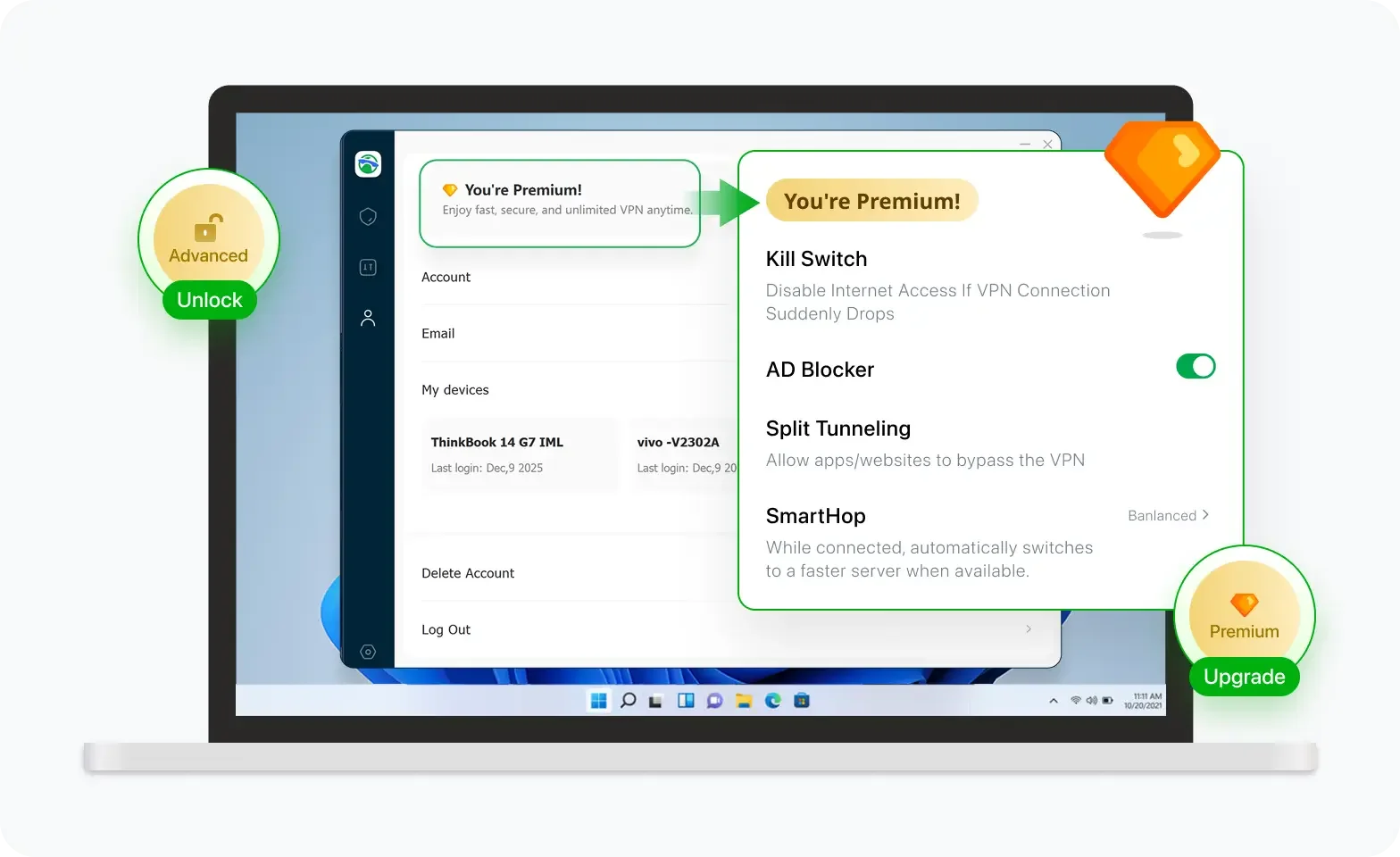
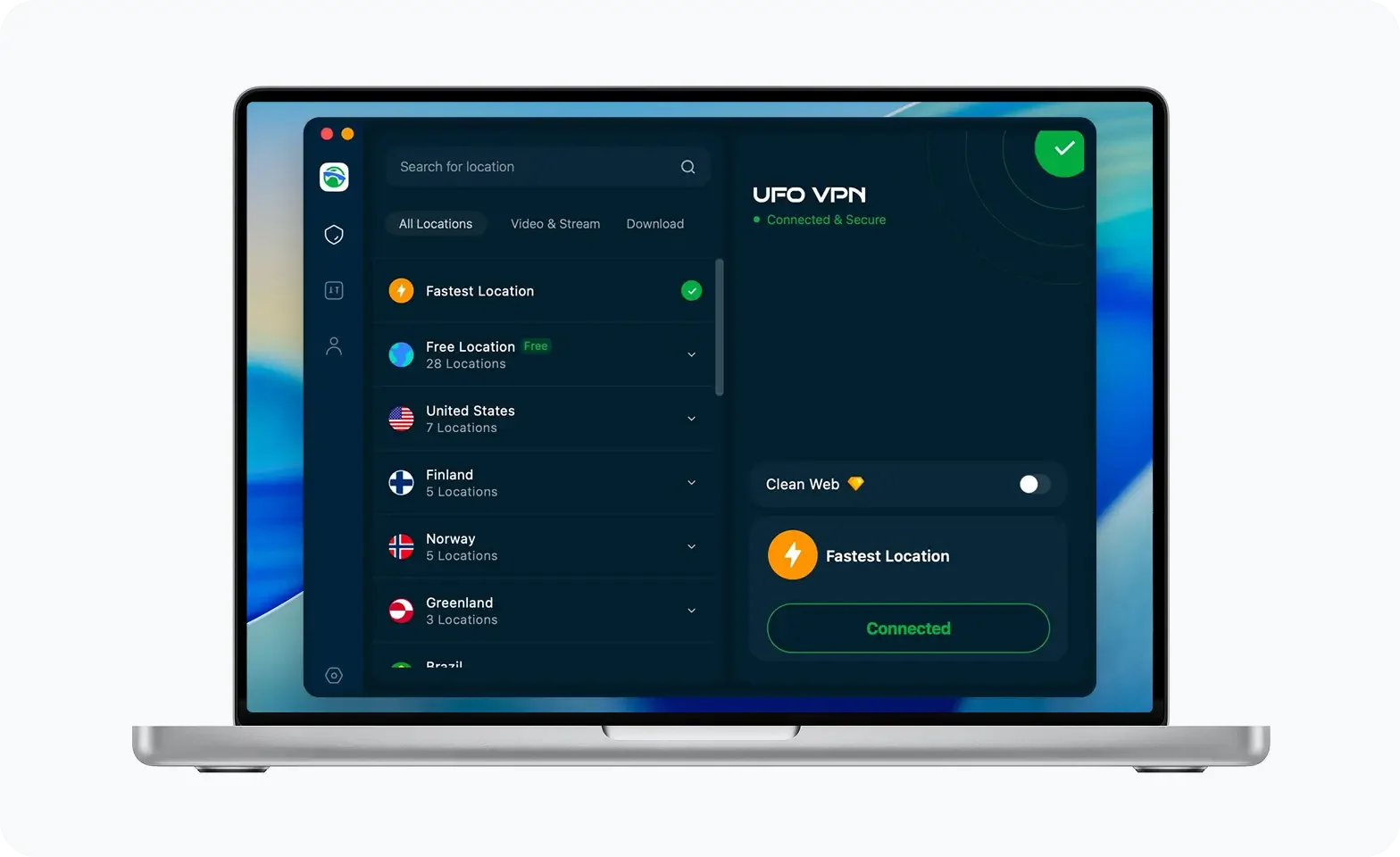
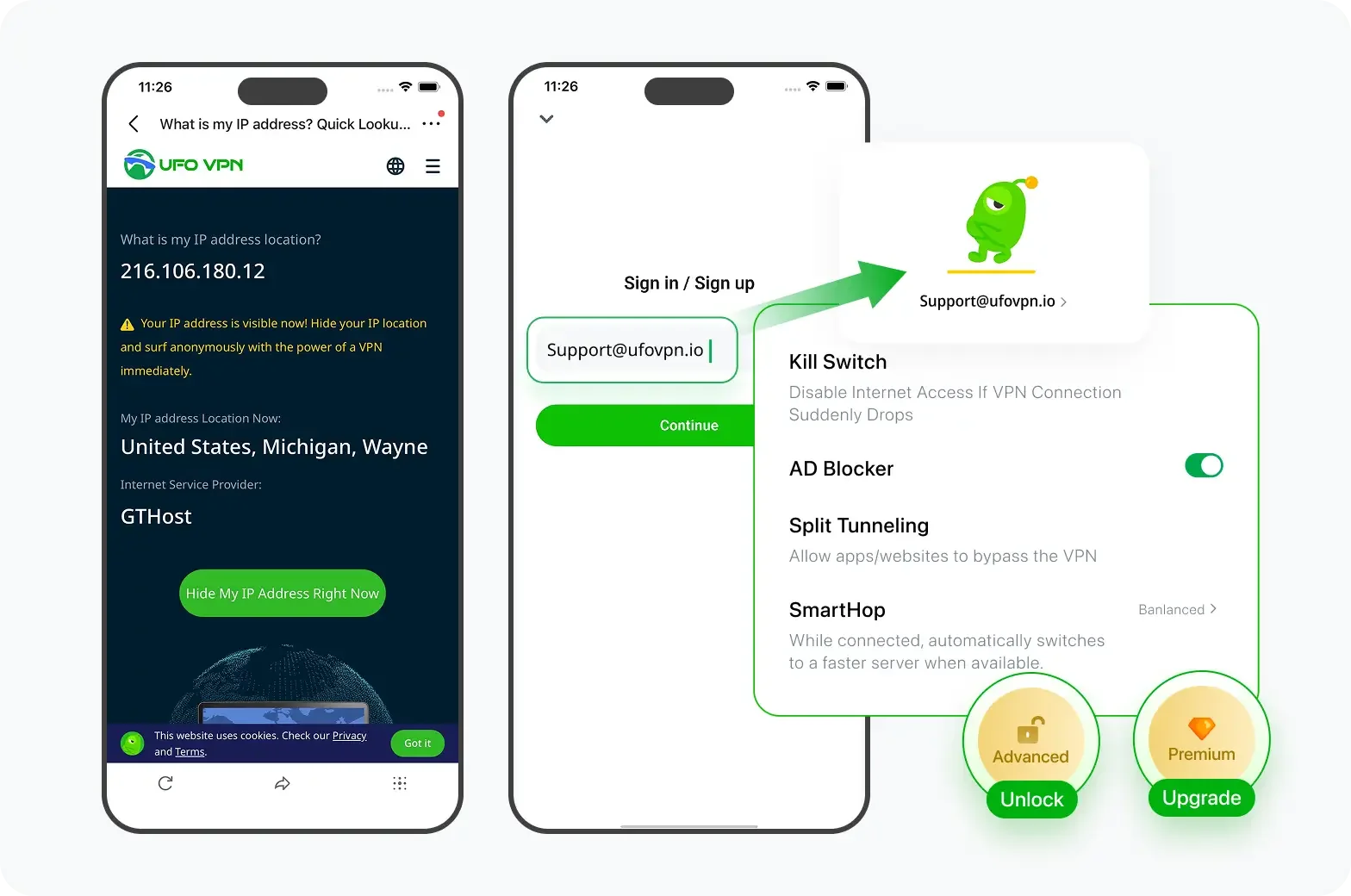
Unlock Pro Features
If you have upgraded to premium plan , feel free to enjoy premium servers for 4K streaming and advanced features like Kill Switch, Split Tunneling, and gaming acceleration. Your Mac is now fully optimized and protected. Inaddition to basic functions, we recommend you turn on

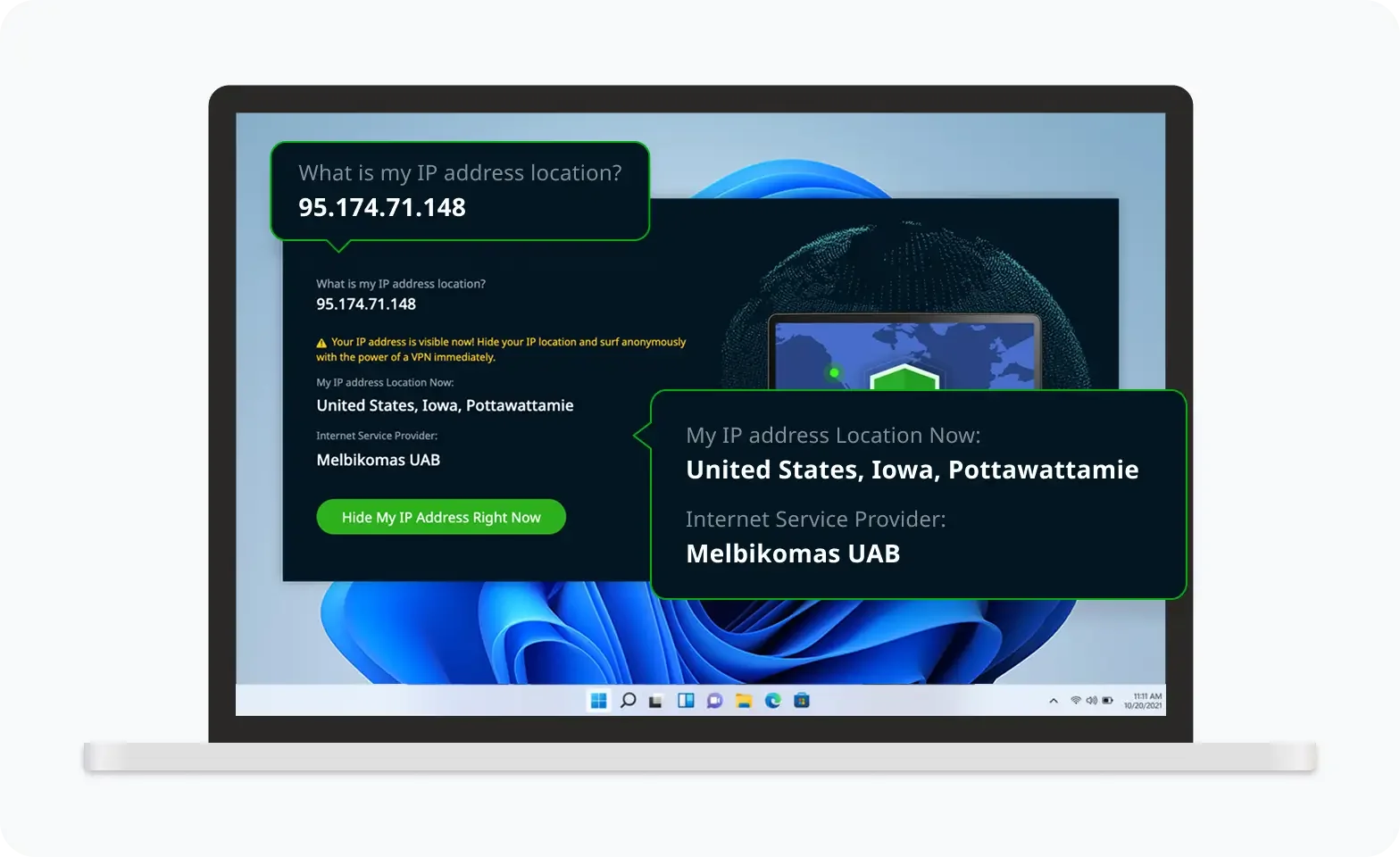
Verify Your IP Now
Use UFO VPN's " What is My IP " feature to see your new IP and location. This confirms your connection is secure, anonymous, and ready for safe browsing online anywhere at any time.

FAQ:
Q1: How does Big Tech impact small businesses?
A1: Big Tech can be both a partner and a competitor to small businesses. Platforms like Amazon and Google offer exposure and tools for marketing, but they can also outcompete small players with their pricing power, data analytics, and control over search rankings or marketplace algorithms.
Q2: Can I completely avoid Big Tech in daily life?
A2: It's extremely difficult to avoid Big Tech entirely, as their services power everything from email to maps and payment processors. However, you can reduce reliance by choosing independent tools like encrypted messaging apps, alternative search engines, and using a VPN like UFO VPN to limit data tracking.
Q3: Why are Big Tech companies involved in so many industries?
A3: Their vast resources and access to user data enable them to expand into areas like healthcare, automotive, and finance. This diversification spreads their influence and ensures continued growth—even if one sector becomes saturated or heavily regulated.
Q4: What is surveillance capitalism and how does it relate to Big Tech?
A4: Surveillance capitalism is a term describing the monetization of personal data through predictive analytics and behavioral profiling. Big Tech companies collect user data to optimize ad targeting, shape online experiences, and drive revenue—often without explicit user consent or full transparency.
Q5: Are Big Tech companies responsible for online misinformation?
A5: While not solely responsible, Big Tech platforms like Facebook and YouTube have been criticized for amplifying misinformation via engagement-driven algorithms. Although steps have been taken to flag or reduce false content, the effectiveness of these measures remains widely debated.
Conclusion
From shaping economies to influencing everyday life, big tech companies occupy a central role in the modern digital landscape. Understanding what is big tech, its benefits, and its pitfalls empowers you to navigate this ecosystem responsibly. Whether you’re concerned about data privacy, market competition, or simply want to explore content from around the globe, a robust VPN solution like UFO VPN ensures you maintain control over your digital footprint and enjoy the internet on your own terms.