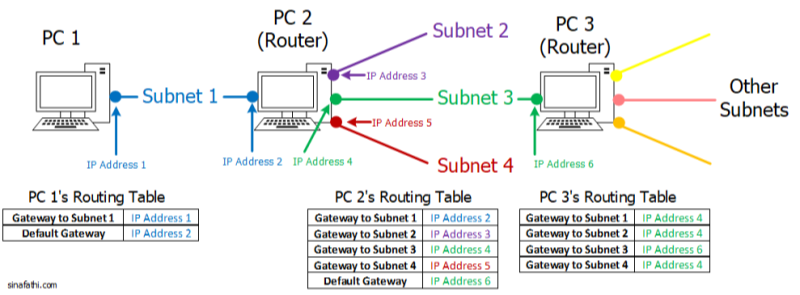
What Is the Gateway IP Address and Gateway in Networking?

A gateway in networking is a device—typically a router—that connects your local area network (LAN) to external networks such as the internet. The gateway IP address is the local IP assigned to that router interface, serving as the “door” your devices use to forward all outbound traffic. When a destination IP doesn’t match any subnet in your routing table, your device sends the packet to the gateway IP, which then routes it onward.
-
Default Gateway: The router’s LAN IP that end devices use by default.
-
Specific Device Gateway: In complex networks, individual subnets or VLANs may have their own gateway addresses.
Gateways can also perform protocol translation, firewall filtering, and network address translation (NAT), making them crucial for both connectivity and security.
Types of Gateway IP Addresses
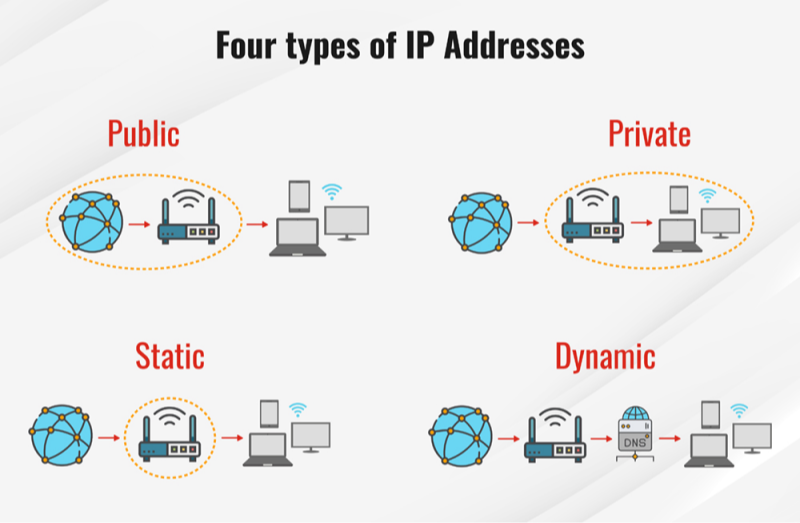
There are two main categories of gateway IP addresses:
-
Default Gateway IP
-
Automatically assigned via DHCP to all devices on a subnet.
-
Example:
192.168.1.1on a typical home network.
-
-
Specific-Gateway (Static) IP
-
Manually configured for special routing scenarios (multiple subnets, DMZ, VLANs).
-
Example:
10.0.0.254serving only servers in a protected subnet.
-
Understanding which type you need ensures devices send traffic to the correct router. Misconfigured gateways lead to “no internet” errors or inaccessible resources.
How to Find Your Gateway IP Address
Locating your gateway IP address varies by operating system and device. Below are the most common methods:
Windows (10/11)
-
Open Command Prompt (Win + R → type
cmd→ Enter). -
Run:
-
Under your active adapter, look for Default Gateway—that’s your gateway IP.
macOS
-
Go to System Preferences → Network.
-
Select your active connection (Wi‑Fi or Ethernet) → Advanced → TCP/IP tab.
-
The Router field shows your gateway IP.
Linux (Ubuntu, Fedora, etc.)
-
Open a terminal.
-
Run:
-
The IP after “default via” is your gateway address.
Android
-
Settings → Network & Internet → Wi‑Fi.
-
Tap your connected network → Advanced.
-
Look for Gateway in the IP details.
iOS (iPhone / iPad)
-
Settings → Wi‑Fi.
-
Tap the ⓘ next to your network.
-
The Router field displays your gateway IP.
Pro Tip: Always secure your router login by changing default credentials. When configuring network settings, use a VPN like UFO VPN: a free proxy VPN to encrypt your login session and protect against snooping.
Understanding and managing your gateway IP address is foundational to network setup, troubleshooting, and security. From finding your gateway on any device to configuring advanced routing and port forwarding, you now have the knowledge—and the secure VPN tool—to take full control. Ready to protect and optimize your network?
⬇️Download UFO VPN today and secure every step of your network management⬇️:
UFO VPN is an all-in-one VPN that offers unlimited access to 4D streaming like Netlfix, Disney Plus, no-ping gaming as PUBG, Roblox, CODM and social networking for YouTube, X, Facebook and more.
Unlock Pro Features
If you have upgraded to premium plan , feel free to enjoy premium servers for 4K streaming and advanced features like Kill Switch, Split Tunneling, and gaming acceleration. Your Mac is now fully optimized and protected. Inaddition to basic functions, we recommend you turn on

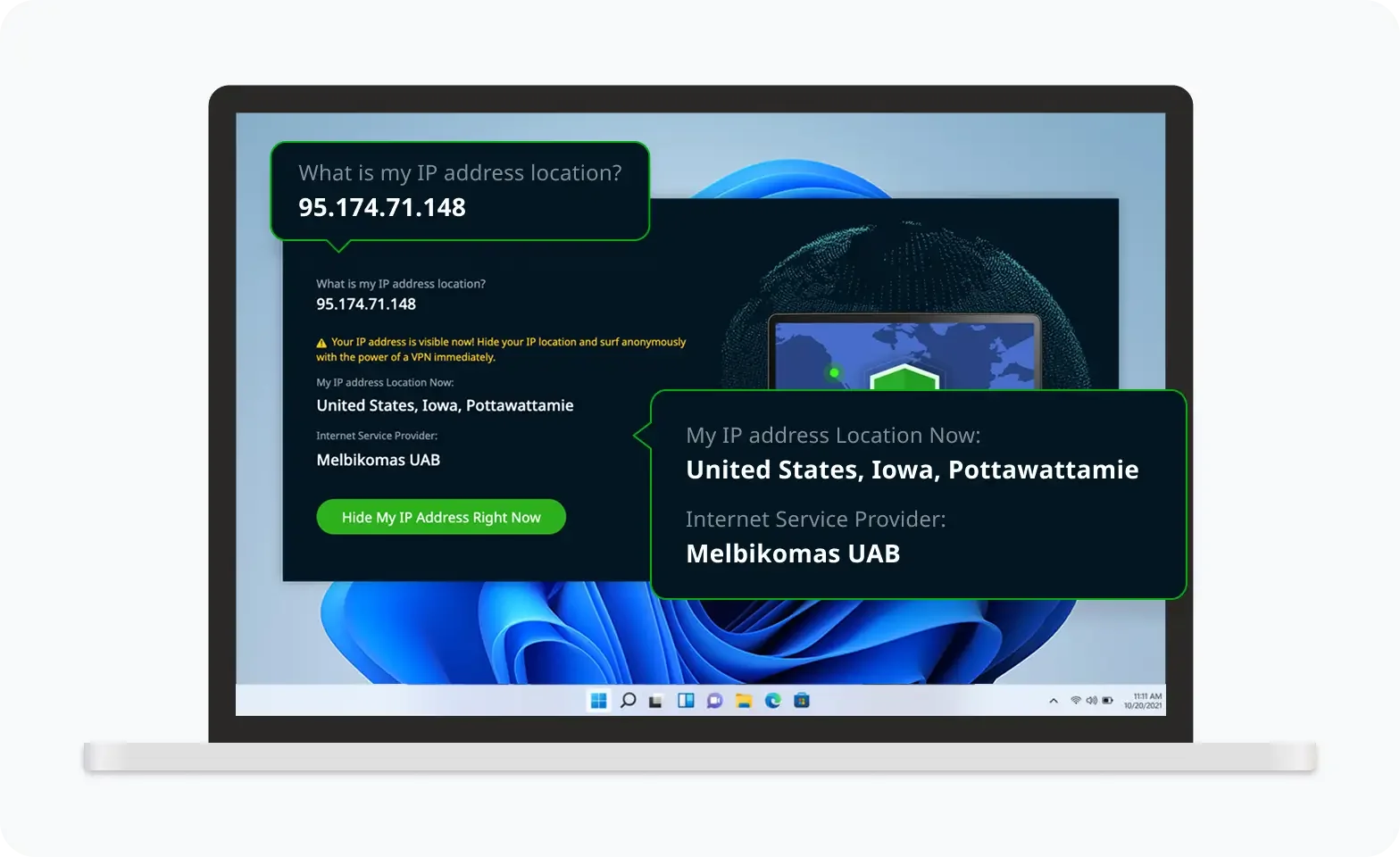
Verify Your IP Now
Use UFO VPN's " What is My IP " feature to see your new IP and location. This confirms your connection is secure, anonymous, and ready for safe browsing online anywhere at any time.

Keep your gateway—and all your internet traffic—safe, private, and lightning‑fast!
What Can We Do With the Gateway IP Address?
Your gateway IP unlocks a wealth of network capabilities:
-
Access Router Admin Panel
-
Enter the gateway IP in a browser (e.g.,
http://192.168.1.1) to configure Wi‑Fi, firewall rules, and DHCP settings.
-
-
Port Forwarding & Remote Access
-
Forward specific ports (HTTP, RDP, gaming) from external requests through your gateway to internal devices.
-
-
Network Diagnostics
-
Ping the gateway IP (
ping 192.168.1.1) to verify local connectivity. -
Use
tracert(Windows) ortraceroute(macOS/Linux) to identify where packets stall.
-
-
Set Static IPs
-
Reserve static leases in your router’s DHCP settings to ensure critical devices keep the same IP.
-
-
Advanced Routing
-
In enterprise or multi‑subnet environments, define static routes on your gateway to control how traffic moves between VLANs or VPN tunnels.
-
-
Network Security
-
Implement access control lists (ACLs) or firewall rules directly on the gateway to block unwanted inbound or outbound traffic.
-
How to Configure a Gateway IP Address
Setting or changing your gateway IP requires router access:
-
Log In to Your Router
-
Open a browser, enter your gateway IP in the address bar.
-
Authenticate with your admin username and password.
-
-
Locate Network Settings
-
Navigate to LAN, Network, or Advanced Settings → LAN Setup.
-
-
Set the Gateway IP
-
Edit the Router IP or Gateway field (e.g., change from
192.168.1.1to192.168.0.254). -
Save or Apply Changes—your router may reboot.
-
-
Update Connected Devices
-
If you use static IPs, update each device’s gateway setting to match the new IP.
-
For DHCP clients, simply reconnect—they will automatically fetch the updated gateway.
-
-
Verify Configuration
-
On a connected device, rerun
ipconfig(Windows) orip route(Linux) to ensure the default gateway reflects the new address.
-
Caution: Misconfiguring your gateway can sever internet access. Always note current settings before changes, and keep a backup of your router’s configuration file.
FAQs
Q1: What Is the Difference Between IP Address and Gateway IP Address?
Your IP address identifies your device on a network. The gateway IP address identifies the router interface that forwards your device’s traffic to other networks.
Q2: Can I Use Any IP as My Gateway?
No—gateway IPs must be on the same subnet as your devices. For a
192.168.1.xnetwork, your gateway should also be192.168.1.y.
Q3: Why Can’t I Access My Router at the Gateway IP?
Possible reasons: wrong IP, firewall blocking, incorrect login credentials, or your device isn’t on the same network. Verify your subnet and try again.
Q4: How Do I Change My Gateway on Windows?
Open Control Panel → Network and Sharing Center → Change adapter settings, right‑click your network → Properties → IPv4 → enter the new gateway under Default gateway.
Q5: Will Changing My Gateway Improve Internet Speed?
Not directly. The gateway IP is just the router’s address. Speed depends on your ISP, router hardware, and network congestion.
Q6: How Does a VPN Affect My Gateway IP?
A VPN encrypts outbound traffic before it reaches your gateway, protecting your network from eavesdropping. For maximum privacy—especially when configuring router settings over remote connections—download and install UFO VPN for your Windows, macOS, Linux, or mobile device.
Q7: Is Gateway IP Address the Same as DNS Server?
No. The gateway routes your packets off‑network; a DNS server resolves domain names to IP addresses. Both can be set on your device or via DHCP.